论文
人心秩序:敬畏特质及其对腐败行为意向的抑制效应
摘要
敬畏特质是一种“人心秩序”,是具有积极力量的心理品质。本研究通过两个子研究探索了敬畏特质对腐败行为意向的影响。研究1采用问卷测量法,结果发现,敬畏特质与腐败行为意向呈显著负相关;研究2通过组合句子任务,启动被试的敬畏特质相关概念,结果发现,敬畏特质启动组被试的腐败行为意向显著低于控制组。研究表明,敬畏特质对腐败行为意向具有显著的抑制效应,能够有效降低个体的腐败行为意向。研究结果符合中国文化中“心存敬畏之心,方能行有所止”的敬畏思想,对“敬畏之心”的培养和腐败行为的减少具有一定的理论与实践意义。
检索正文关键字
论文目录
-
一 引言
- (一)敬畏特质
- (二)敬畏特质与腐败行为
-
二 研究1:敬畏特质与腐败行为意向的关系
- (一)被试
- (二)研究工具
- 1.敬畏特质量表
- 2.腐败行为意向量表
- 3.社会赞许性量表
- (三)结果
- 1.共同方法偏差检验
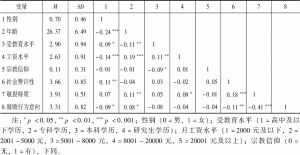
- 2.描述和相关分析
- 3.敬畏特质与腐败行为意向的关系
- (四)讨论
-
三 研究2:敬畏特质启动对腐败行为意向的影响
- (一)被试
- (二)实验设计和程序
- (三)实验材料
- 1.敬畏特质词汇
- 2.腐败行为意向
- 3.控制变量
- (四)结果
- (五)讨论
- 四 讨论与结论
相关文献
宽容对小学生外化问题行为的影响:友谊质量、敌意归因的中介作用
程序公平性和结果有利性对儿童程序正义判断、结果满意度与权威接纳意愿的影响
查看更多>>>