论文
宜人性之殇:收入不平等对国家宜人性人格与国民健康指标间关系的系列负性调节效应
摘要
人格一直被认为是影响健康的重要因素,而诸多有关宜人性人格与健康关系的研究结论间常有殊异之处。缺少考量人格特质与宏观环境的交互性,可能是宜人性和健康关系尚不十分明确的主要原因之一。赖凯声和陈浩(2020)基于美国州际区域水平数据分析,发现收入不平等对宜人性和健康间关系具有明显负向调节作用,即宜人性人格与收入不平等环境具有消极亲和性。本研究进一步在国家水平上检验该结论,结果显示,国家收入不平等程度在国家宜人性人格与多项国民身心健康指标之间,呈现系列显著负性调节效应,再次确认“宜人性之殇”现象的存在。作为表达友善、他人取向和合作倾向的人格特征,高宜人性在特定社会生态环境中(如高收入不平等),会有严重的健康代价;这一发现将启发研究者对道德实践与情境关系议题的讨论。
作者
陈浩 ,南开大学社会心理学系副教授,中山大学广州粤港澳社会心理建设研究中心研究员。
洪斌 ,南开大学社会心理学系硕士研究生。
赖凯声 ,暨南大学新闻与传播学院教授,主要研究方向为网络社会治理、传播心理学、大数据舆情。
参考文献 查看全部 ↓
检索正文关键字
论文目录
-
一 引言
- (一)宜人性人格和个体健康
- (二)宜人性人格区域空间分布和国民健康指标间关系
- (三)收入不平等宏观环境的心理后效及其对健康的影响
- (四)本研究假设
-
二 研究方法
- (一)变量选取和数据来源
- (二)分析程序和方法
-
三 结果分析
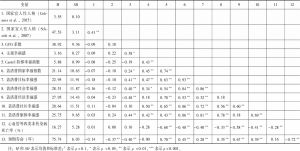
- (一)国家宜人性人格和国民身心健康系列指标间的关联
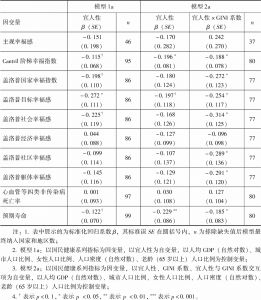
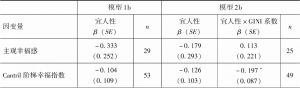
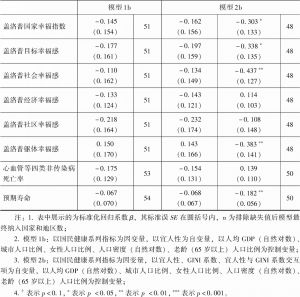
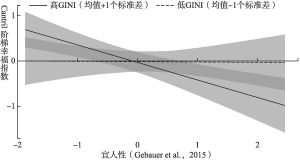
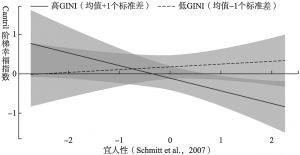
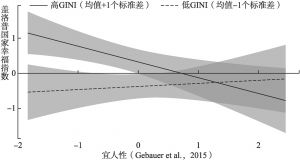
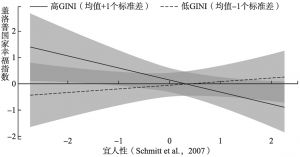
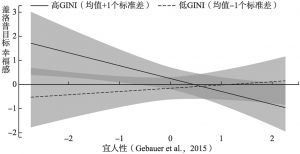
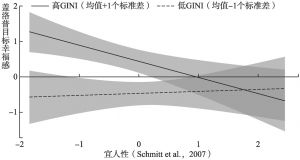
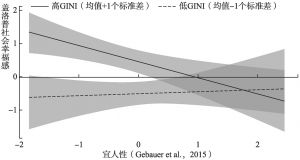
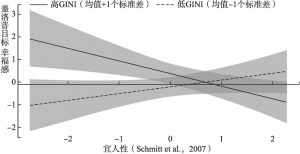
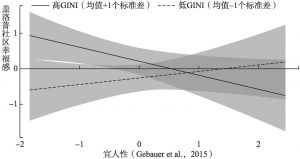
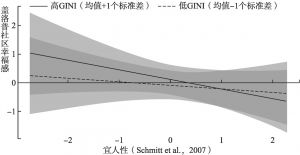
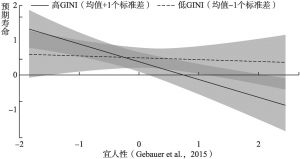
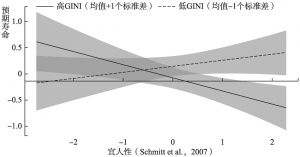
- (二)GINI系数的调节效应分析
- 四 讨论
相关文献
宽容对小学生外化问题行为的影响:友谊质量、敌意归因的中介作用
程序公平性和结果有利性对儿童程序正义判断、结果满意度与权威接纳意愿的影响
查看更多>>>