报告
数字经济引领绿色发展的效应、机制与路径选择
摘要
自第一次工业革命以来,煤、石油、天然气等化石能源的发现和利用极大地推动了经济社会的发展,同时也带来了严重的环境污染和气候变化问题,尽早实现“碳达峰、碳中和”已经成为保护地球家园的全球共识。随着数字技术(Digital Technology)在生产生活中的创新应用,数字技术对实现碳中和的作用日益受到关注。一方面,以云计算、大数据和物联网等为代表的数字技术有望重塑企业生产流程和能源系统,从而大幅提升能源利用效率,直接助力行业减少碳排放;另一方面,数字技术衍生的新业态、对经济结构和能源结构的优化以及对消费者生活和消费方式转变的促进,均可间接助力“碳达峰、碳中和”的实现。为了系统研究这个问题,本文首先分析数字设备、数字技术和数字产业发展对能源消费和绿色经济发展的影响机制。其次全面阐述数字经济对绿色发展的途径和有益探索。最后从中国企业的实践出发,总结京东集团的探索及其为数字经济促进行业和地区减排做出的表率作用,以期为未来实现节能减排提供有益的借鉴。
作者
何德旭 ,研究员,中国社会科学院财经战略研究院院长。中国社会科学院大学商学院院长、教授、博士生导师。国家社会科学基金学科评审组专家,中国金融学会常务理事,中国财政学会常务理事,中国农村金融学会副会长。享受国务院政府特殊津贴。入选中宣部文化名家暨“四个一批”人才工程。主持完成国家社会科学基金重大项目、国家社会科学基金重点项目、中国社会科学院重大项目等国家级和省部级重大课题十余项。出版和发表成果逾二百部(篇),多项研究成果获省部级优秀科研成果奖。主要研究方向为金融制度、货币政策、金融创新、金融安全、资本市场、公司融资、数字经济。
王振霞 ,经济学博士,副研究员,中国社会科学院财经战略研究院研究室主任,主要研究方向为宏观经济学、价格理论。
闫冰倩 ,经济学博士,中国社会科学院财经战略研究院副研究员,主要研究方向为投入产出分析、宏观经济建模分析、全球价值链与环境。
王蕾 ,中国社会科学院工业经济研究所副研究员,主要研究方向为能源政策、能源效率和能源转型等。
检索正文关键字
报告目录
-
一 “双碳”战略背景下数字经济引领绿色发展的效应与机制
- (一)数字经济和数字技术对绿色发展的效应研究
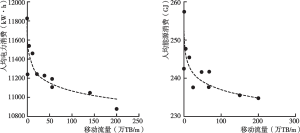
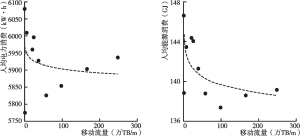
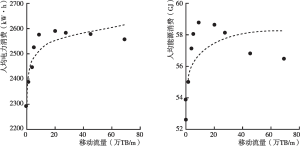
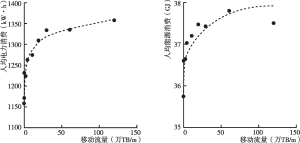
- 1.数字经济和数字技术能源效应的实证研究与相关测算
- 2.数字技术和数字设备能源效应的典型事实和经济理论
- (二)数字经济引领绿色发展的机制
- 1.数字技术助力行业直接减少碳排放
- 2.数字技术助力行业间接减排
- 3.数字技术助力行业减少碳排放的补充效应
- (三)数字技术应用助力减排的难点和问题
- (一)数字经济和数字技术对绿色发展的效应研究
-
二 “双碳”战略背景下数字经济引领绿色发展的路径选择
- (一)数字技术和数字设备精准识别和预测减排
- 1.大数据技术促进碳排放精准计量及预测
- 2.AI技术促进能源高效调度利用
- 3.数字孪生技术推动实现碳排放的精准监测与规划
- (二)数字技术和数字设备促进高碳行业的节能减排
- 1.运输部门
- 2.建筑和制造部门
- (三)数字技术和数字设备促进产品生产普遍低碳化
- (一)数字技术和数字设备精准识别和预测减排
-
三 中国企业引领绿色发展的探索——以京东的实践为例
- (一)出台企业低碳发展的具体目标
- (二)绿色低碳数据中心和绿色供应链体系
- 1.产品绿色采购
- 2.产品绿色包装
- 3.商品绿色运输
- 4.产品绿色仓储
- (三)赋能其他行业和地区,促进共同减排
- 1.智能商砼供应链平台
- 2.AI火力发电
- 3.云秸秆焚烧监测系统
- (四)倡导绿色办公、绿色出行和绿色消费
- 四 数字经济促进绿色发展的政策建议
相关文献
查看更多>>>