论文
政治嵌入对于反腐败信心的影响
摘要
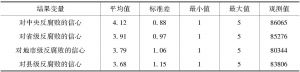
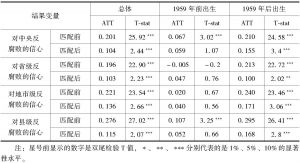
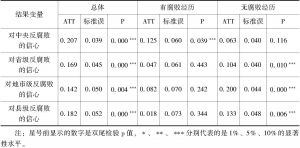
现有研究表明,政治嵌入与清廉感知存在相关性。但是,政治嵌入本身存在选择效应,即选择被吸纳到政治体制的人本身可能就具有对于体制的信心,而组织也会选择有特定特征的个体。因而,必须剔除掉选择效应之后,才能准确评估政治嵌入本身对反腐败信心的影响。本文采用倾向得分匹配的方法,通过分析2017年全国廉情调查数据发现,在控制选择效应的情况下,政治嵌入对于各级政府的反腐败信心的影响略微有所下降,但都始终存在积极且显著的影响。而且,与有索贿经历的个体相比,没有索贿经历的个体的政治嵌入对于反腐败信心的积极影响更为显著。此外,不同类型的公共部门的政治嵌入对反腐败信心的影响也有差异性,呈现出横向的差序格局。其中,党政部门政治嵌入的积极影响最为显著,而国企最弱。
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 问题的提出
-
二 研究设计
- (一)文献回顾以及研究假设
- 1.政治嵌入与反腐败信心
- 2.腐败经历对于政治嵌入与反腐败信心关系的影响
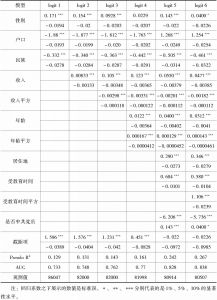
- (二)统计建模
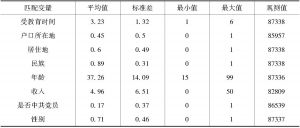
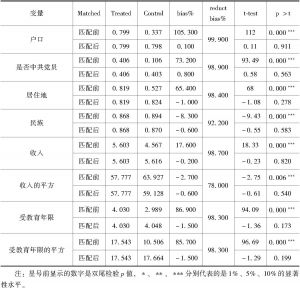
- (三)数据来源
- (一)文献回顾以及研究假设
- 三 描述统计
-
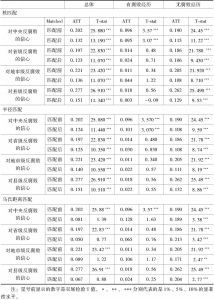
四 分析结果以及检验
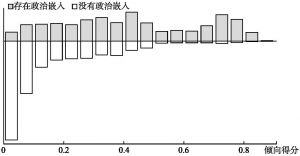
- (一)平行假设检验
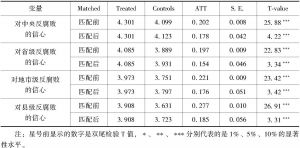
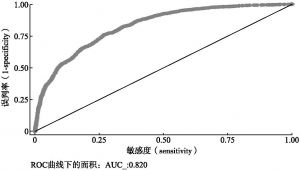
- (二)共同支撑假设检验
-
五 稳健性检验
- (一)其他匹配方法
- (二)分组匹配
- (三)自抽样
- 六 结论
相关文献
查看更多>>>