章节
风险投资和创业企业总是完美一对吗
关键词
作者
罗超亮 ,贵州财经大学工商学院讲师、管理学博士,研究方向为战略管理、风险投资。在《中山大学学报》《南开管理评论》等期刊上发表多篇论文,现主持国家自然科学基金青年项目1项,参与国家自然科学基金项目多项。
符正平 ,教授,中山大学自贸区综合研究院院长,兼粤港澳发展研究院副院长,研究方向:产业组织与管理、区域发展战略与管理。
刘冰 ,中山大学旅游学院副教授、管理学博士、硕士生导师。主要研究领域为战略管理、旅游管理、风险投资、社会网络。在Tourism Management、《南开管理评论》、《旅游学刊》等期刊发表多篇论文。主持并完成国家自然科学基金项目和国家社会科学基金项目多项。
王曦 ,南华大学经济管理与法学学院讲师,管理学博士。主要研究领域为战略管理、风险投资、社会网络。在《西北工业大学学报》《山西财经大学学报》等CSSCI期刊上发表论文近10篇。主持湖南省社会科学基金项目1项,参与国家自然科学基金项目多项。
检索正文关键字
章节目录
-
第一节 引言
- 一 研究背景
- 二 研究问题
-
第二节 理论基础和研究假设
- 一 冗余资源和创业企业绩效的关系
- (一)冗余资源和创业企业绩效的关系
- 二 风险投资机构的介入对冗余资源和创业企业绩效关系的影响
- 三 风险投资机构的介入程度对冗余资源和创业企业绩效关系的影响
- 一 冗余资源和创业企业绩效的关系
-
第三节 研究设计
- 一 数据搜集
- 二 变量测量
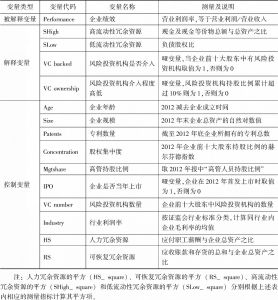
- (一)被解释变量
- (二)解释变量
- (三)控制变量
-
第四节 实证分析及结果
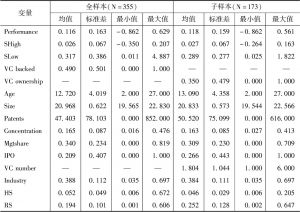
- 一 描述性统计结果
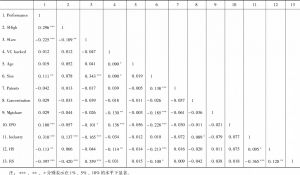
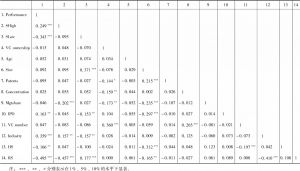
- 二 相关系数分析结果
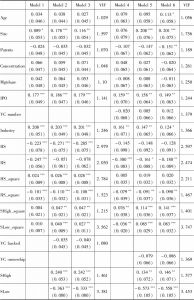
- 三 多元回归分析结果
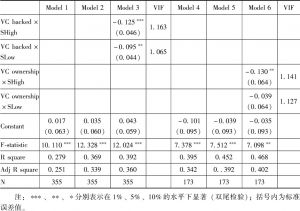
- 四 共线性、内生性问题及其他稳健性检验
- (一)共线性问题说明
- (二)内生性问题说明
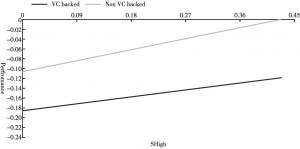
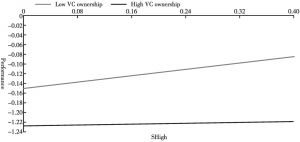
- (三)稳健性检验
-
第五节 结论与讨论
- 一 主要结论
- 二 理论贡献
- 三 管理启示及政策建议
- 四 进一步讨论及研究展望
相关文献
查看更多>>>