章节
真实进步指标理论综述
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 2.1 引言
-
2.2 真实进步指标的理论与测算思路
- 2.2.1 真实进步指标理论的诞生与发展
- 2.2.1.1 GDP对福利的测度
- 2.2.1.2 GDP对福利测度的不足
- 2.2.1.3 GDP的调整及替代指标
- 2.2.1.4 GPI的产生与发展
- 2.2.2 GPI指标的测算思路
- 2.2.2.1 GPI的目标任务
- 2.2.2.2 可持续经济福利的含义
- 2.2.2.3 GPI测算的理论来源
- 2.2.2.4 GPI的设计结构
- 2.2.1 真实进步指标理论的诞生与发展
-
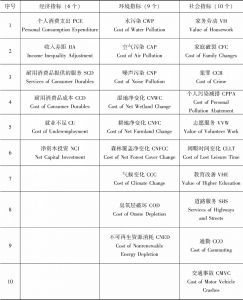
2.3 GPI的指标设置
- 2.3.1 指标设置——以美国佛蒙特州为例
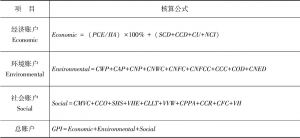
- 2.3.1.1 GPI 1.0核算的公式
- 2.3.1.2 经济指标
- 2.3.1.3 环境指标
- 2.3.1.4 社会指标
- 2.3.1.5 总结
- 2.3.2 GPI 2.0指标设置——以巴尔的摩市为例
- 2.3.2.1 GPI 2.0核算的公式
- 2.3.2.2 以市场为基础的商品和服务
- 2.3.2.3 要素资本提供的服务
- 2.3.2.4 环境和社会成本
- 2.3.2.5 结论
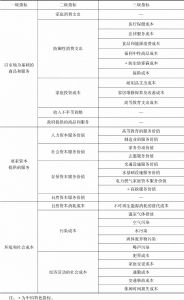
- 2.3.3 中国真实进步指标报告指标设置
- 2.3.3.1 中国真实进步指标体系核算项目
- 2.3.3.2 以市场为基础的商品和服务
- 2.3.3.3 要素资本提供的服务
- 2.3.3.4 环境和社会成本
- 2.3.1 指标设置——以美国佛蒙特州为例
-
2.4 GPI的应用
- 2.4.1 国家、地区应用
- 2.4.1.1 国家、地区应用综述
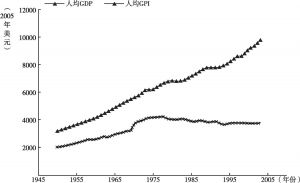
- 2.4.1.2 GPI:全球真实进步对比
- 2.4.1.3 GPI:国家真实进步衡量
- 2.4.1.4 GPI:地区真实进步衡量
- 2.4.1.5 总结
- 2.4.2 基于GPI核算的政策评估
- 2.4.2.1 巴尔的摩市雨水管理计划的实施背景
- 2.4.2.2 巴尔的摩市雨水管理计划的经济价值
- 2.4.1 国家、地区应用
-
2.5 GPI评价与前景
- 2.5.1 GPI的优点
- 2.5.2 GPI的不足
- 2.5.3 前景与改进
查看更多>>>