章节
欧盟与全球金融治理
摘要
2008年的金融危机暴露了国际金融体系的缺陷,各国意识到应加强国际合作,积极参与全球金融治理。欧盟是其中重要的参与者和执行者,在全球金融治理尤其是全球金融监管中发挥了不可替代的作用,但也面临着缺乏凝聚力、难以形成统一立场的问题。国际金融机构改革是危机后G20推动的重点议题之一,欧盟在国际货币基金组织改革中表现得比较被动,整体影响力下滑。在国际储备货币方面,欧元曾被认为是美元有力的竞争者,但制度上的缺陷使之很难取代美元的地位。在全球金融监管机制改革合作中,欧盟长期持积极参与和引导的立场,并发挥了难以替代的作用。
检索正文关键字
章节目录
-
一 全球金融治理发展及其研究综述
- (一)全球金融治理发展
- (二)全球金融治理研究综述
-
二 欧盟在全球金融治理中的角色与挑战
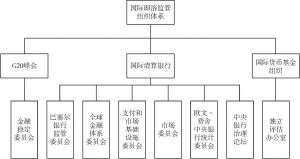
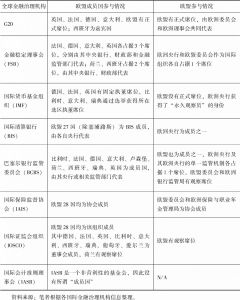
- (一)欧盟参与全球金融治理机构情况
- (二)欧盟在全球金融治理中的地位和面临的挑战
-
三 欧盟与国际金融机构改革
- (一)国际货币基金组织改革的背景
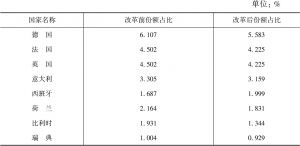
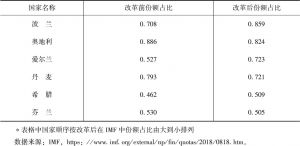
- (二)IMF改革对欧盟的影响
-
四 欧盟与全球储备货币体系调整
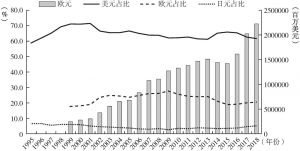
- (一)欧元在国际储备货币格局中的地位演变
- (二)欧元在国际储备货币中的挑战与困境
-
五 欧盟与全球金融监管体系治理
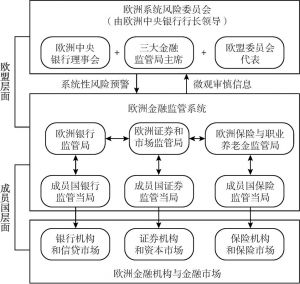
- (一)欧盟(欧洲)内部金融监管改革
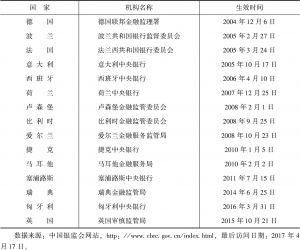
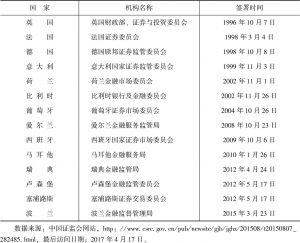
- (二)欧盟参与全球金融监管合作
- (三)欧盟与中国金融监管体制合作
-
六 有关欧盟与全球金融治理未来发展的几点展望
- (一)逆全球化浪潮将阻碍全球金融治理发展
- (二)英国脱欧会削弱欧盟的金融实力和欧盟对全球金融治理的影响力
- (三)金融监管仍将是欧盟参与全球金融治理的优势领域
相关文献
查看更多>>>