章节
中国地方政府公共财政支出行为和城市预算外土地收入
摘要
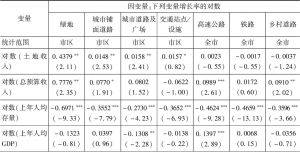
本文提出了一种间接方法来考察地方政府对于土地收入的支出偏好。这种方法对公共部门产出与土地收入进行回归。土地收入是预算外收入的最主要来源。本文采用这种方法能够克服无法获得土地收入的支出数据的问题。实证研究得出的结论是,地方政府更愿意将土地收入用于城市生产性基础设施建设(如城市铺面道路建设),投资于形象工程(如打造开放空间和公共广场)以及有助于加深公众对地方经济增长印象的项目。本文使用1999~2006年中国地级市的面板数据检验了这些假设。回归结果证实了这些假设。
关键词
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 引言
- 一 文献
-
二 地方政府财政状况和预算外土地收入
- (一)财政状况
- (二)土地制度和土地租赁
- (三)预算外收入和土地收入
- (四)土地收入和城市基础设施
- 三 模型和数据
- 四 实证结果
- 五 结语
相关文献
查看更多>>>