章节
建筑限高、土地开发和经济成本
摘要
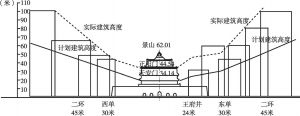
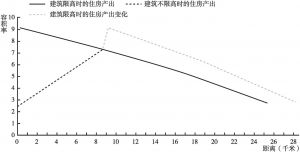
北京具有独特的空间格局,其特点是建筑高度呈倒U形曲线,交通网络呈几何发展(环形公路及轴向道路)。建筑高度的倒U形曲线主要是内城出于历史保护的目的而限制建筑高度的结果。本文利用土地开发数据对建筑限高的经济成本进行了估算,通过模拟无建筑限高的土地开发和有建筑限高的土地开发,发现建筑限高的经济成本是巨大的。建筑限高的影响包括市中心的土地价格跌幅高达60%,住房产出下降70%,资本密度下降85%。为了弥补房屋产出量的损失,不得不扩张城市边缘。为了抵消建筑空间减少所带来的负面影响,房价上涨了20%,城市边缘扩张了12%。最后,建筑限高导致了城市的无序蔓延和低密度发展。
关键词
作者
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 引言
-
一 城市土地利用法规与城市空间发展
- (一)建筑限高和分区
- (二)北京的中央商务区:一个土地开发受限案例
-
二 模型设定
- (一)无建筑限高的土地市场和城市发展
- (二)实施规划干预的土地市场与城市发展
-
三 土地利用管制的经济成本
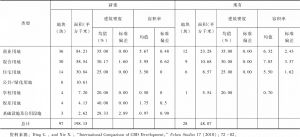
- (一)研究区域和数据
- (二)北京的城市发展模式
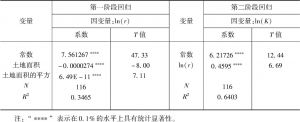
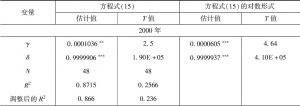
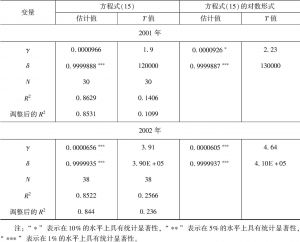
- (三)住房生产函数
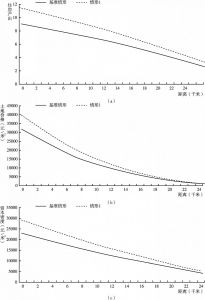
- (四)建筑限高/不限高时的土地开发模式
- (五)建筑限高对土地开发的影响
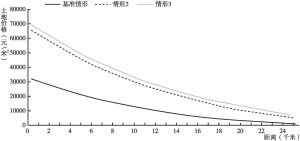
- (六)资本-土地替代弹性对土地开发的影响
- (七)房价上涨对土地开发的影响
- (八)容积率限制对城市无序扩张的影响
- 四 结论
相关文献
查看更多>>>