章节
社会创业推动乡村脱贫的模式探索
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 一 研究背景
-
二 乡村社会创业脱贫的福利分析与实践
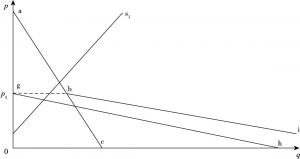
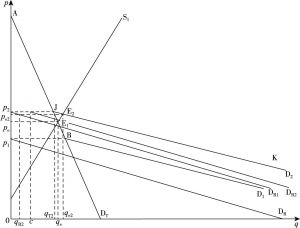
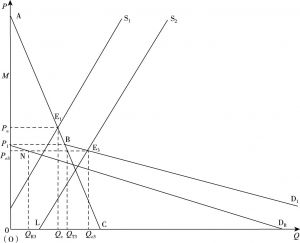
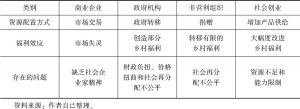
- (一)现有乡村脱贫方式的资源配置作用
- (二)乡村社会创业脱贫方式的资源配置作用
- (三)乡村脱贫资源配置方式的福利效应比较
- (四)乡村社会创业脱贫实践
- 1.乡村社会事业:拼多多电商“多多农园”项目
- 2.政府衍生的乡村社会企业:内蒙古金融扶贫富民工程
- 3.乡村非营利组织创业:贵州纳桑红糖项目
- 4.原生型乡村社会企业:深圳市诚信诺科技有限公司
-
三 乡村社会创业脱贫的机制和模式
- (一)社会创业是实现乡村脱贫的有效方式
- 1.社会创业激活乡村贫困地区创富意识
- 2.社会创业促使乡村贫困地区产品结构调整
- 3.社会创业提高乡村贫困人口劳动技能
- 4.社会创业实现乡村贫困地区人才回流
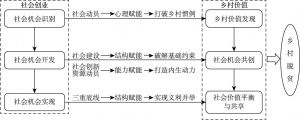
- (二)社会创业推动乡村脱贫的机制构建
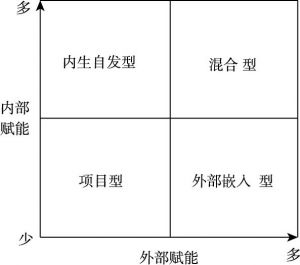
- (三)基于赋能视角的乡村脱贫社会创业模式
- 1.项目型乡村社会创业模式:西吉县清源和谐社区服务中心
- 2.外部嵌入型乡村社会创业模式:SEE沙漠小米
- 3.内生自发型乡村社会创业模式:水之源农产品产销专业合作社
- 4.混合型乡村社会创业模式:四川十八湾农业发展有限公司
- (四)乡村社会创业脱贫实践的不足
- (一)社会创业是实现乡村脱贫的有效方式
-
四 乡村社会创业脱贫的政策组合
- (一)大力发挥社会企业家精神,培育和壮大乡村社会企业家群体
- (二)鼓励乡村多元创新,推动包容式发展
- (三)培育乡村市场发展的各类市场要素,构建良好乡村价值生态
- (四)推动数字技术与社会创业融合,提高数字技术对乡村贫困地区的赋能作用
- (五)加强乡村社会创业顶层设计,构建合法性机制
相关文献
查看更多>>>