章节
“区块链+”:赋能公益组织扶贫
检索正文关键字
章节目录
-
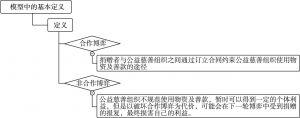
一 我国社会公益慈善事业的主要问题及深入分析
- (一)主要问题
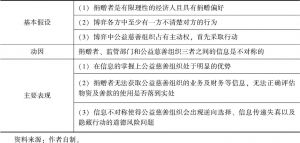
- 1.各相关方诚信的缺失
- 2.公益领域求助信息的发布受限于发布平台
- 3.善款流转的服务费用
- 4.慈善组织行政化和监管问题
- 5.我国社会公益慈善的名义水平与道德风险
- (二)影响社会公益的要素归纳和现行政策分析
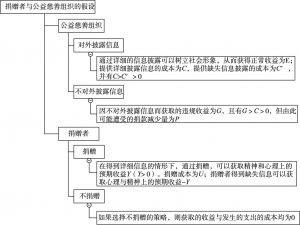
- (三)影响社会公益事业要素的量化分析
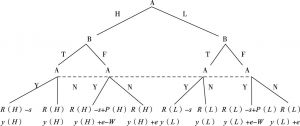
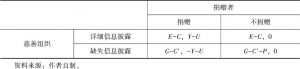
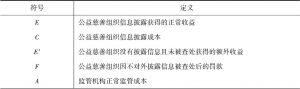
- 1.现行社会公益慈善中的静态博弈
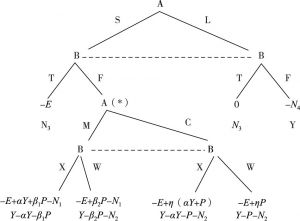
- 2.现行社会公益慈善中的动态博弈
- (一)主要问题
-
二 “区块链+”构建我国新型社会公益慈善体系的分析
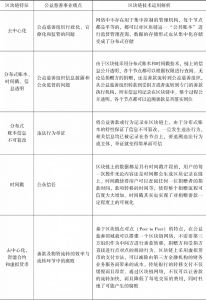
- (一)“区块链+”解决的公益慈善事业痛点
- (二)采用“区块链+”的社会公益慈善体系的博弈分析
- 1.引入区块链后的捐赠者与公益慈善组织的博弈分析
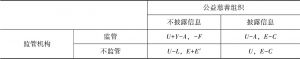
- 2.引入区块链后的公益慈善组织与监管机构间的博弈分析
- (三)“区块链+”背后的博弈论和经济学原理
- 1.直观表象
- 2.深层次的博弈论和经济学原理
-
三 区块链在发达国家或组织的社会公益慈善运用实证研究
- (一)在区块链上运行的约旦难民营
- 1.难民及难民营背景介绍
- 2.世界粮食计划署(WFP)
- 3.相关技术储备
- 4.公共援助和对外援助
- (二)英国
- 1.项目背景
- 2.项目指导书
- 3.项目实施情况
- (三)美国Austin市
- 1.项目背景
- 2.项目指导书
- 3.项目实施
- 4.上链的基础工作
- (四)芬兰
- (五)实证分析
- (一)在区块链上运行的约旦难民营
-
四 中国“区块链+”公益试行效果分析与政策建议
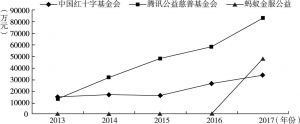
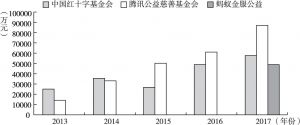
- (一)国内企业“区块链+公益”试行状况
- (二)分析及建议
-
五 我国开展“区块链+”民生应用的一些启示
- (一)我国开展“区块链+”赋能扶贫的设想
- (二)启示:要高度重视技术进步,尤其是区块链
- 附录一:缩略语
相关文献
查看更多>>>