论文
重复投资有利于知识溢出?
摘要
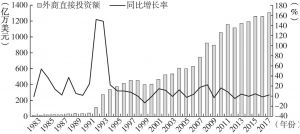
科斯在《变革中国——市场经济的中国之路》中提出,重复投资虽然导致有形资本的浪费,但它对生产技术在中国的传播以及工人技术的提高起到相当大的作用。为验证该观点,本文基于珠三角私营企业主和个体工商户访谈、2014年中国劳动力动态调查数据、国家统计局数据,进一步梳理与分析重复投资和知识溢出的关系。研究发现:(1)重复投资与知识溢出存在双向互动关系,不同改革阶段,重复投资效用不同,科斯观点部分符合中国经济发展实际;(2)重复投资与知识溢出的相互影响分别受制于不同的因素,且在不同行业存在差异;(3)要跳出低技术水平重复投资陷阱,关键在于提高基础研发能力与加大知识产权保护力度。文章最后扩展讨论了科斯观点对中国创新的启示。
作者
朱艳婷 ,南京大学社会学系博士研究生。
叶宸辰 ,南京大学社会学系硕士研究生。
Zhu Yanting
Ye Chenchen
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 引言
- 二 文献回顾
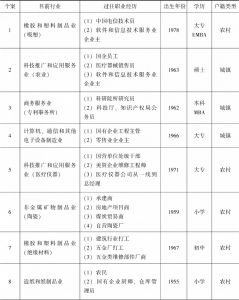
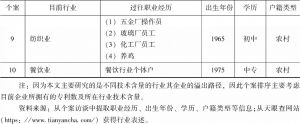
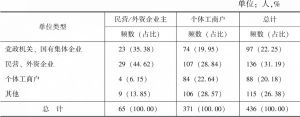
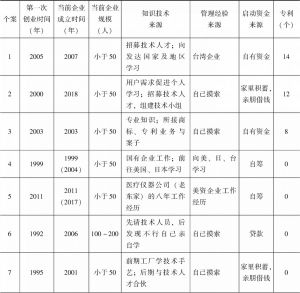
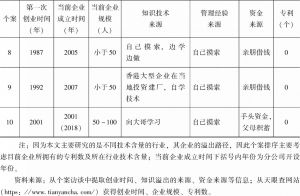
- 三 研究方法、数据及个案介绍
-
四 老板的诞生:创业环境和溢出轨迹
- (一)创业环境
- (二)溢出轨迹
-
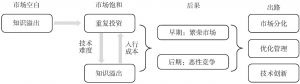
五 老板游戏:繁荣市场还是恶性竞争?
- (一)知识溢出与重复投资双向互动
- (二)不同时期的重复投资效用
-
六 胜者为王:生存策略和长久之计
- (一)生存策略
- (二)长久之计
- 七 结论与讨论
相关文献
查看更多>>>