章节
静态GTAP理论
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 1.1 前言
-
1.2 模型概览
- 1.2.1 无税封闭经济
- 1.2.2 无税开放经济
-
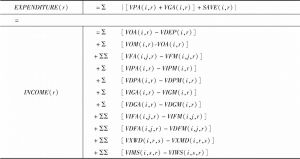
1.3 绝对量之间的核算关系
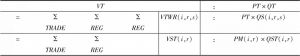
- 1.3.1 区域市场的销售分配
- 1.3.2 居民消费的来源
- 1.3.3 厂商购买来源和居民要素收入
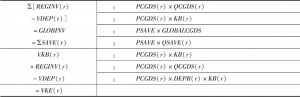
- 1.3.4 分配和区域收入来源
- 1.3.5 全球部门
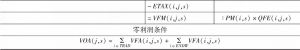
- 1.4 平衡条件和局部均衡闭合
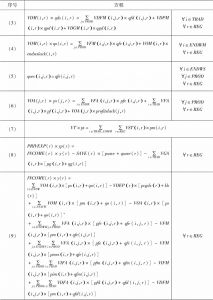
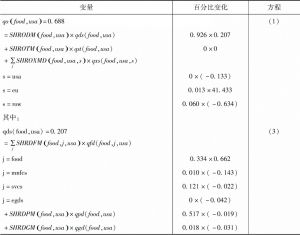
- 1.5 核算方程的线性化表示
-
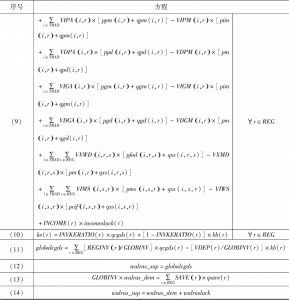
1.6 行为方程
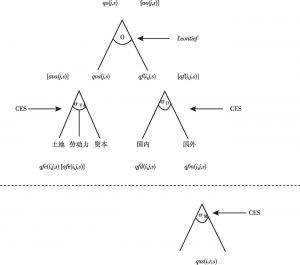
- 1.6.1 生产者行为
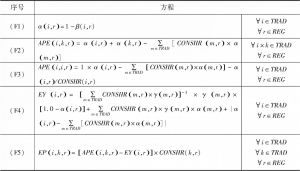
- 1.6.2 行为方程
- 1.6.3 关税改革的影响
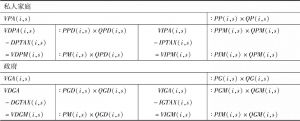
- 1.6.4 居民行为
- 1.6.4.1 理论
- 1.6.4.2 方程
- 1.6.4.3 政府需求
- 1.6.4.4 私人需求
- 1.6.4.5 非完全流动性生产要素
- 1.6.4.6 宏观经济闭合
- 1.6.4.7 固定资本形成和各区域投资分配
- 1.6.5 全球运输
- 1.6.6 概要指数
- 1.7 一个简单的量化示例
- 1.8 总结
- 注释
查看更多>>>