章节
从个体情绪到总体性情绪:关于工作满意度的研究
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 一 问题的缘起
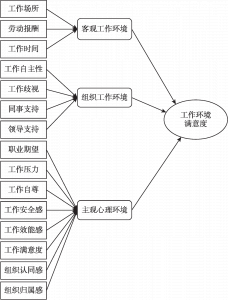
- 二 工作环境的定义及内涵
-
三 研究设计
- (一)分析策略
- (二)问卷设计
- (三)数据来源与样本描述
-
四 数据分析
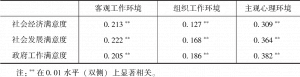
- (一)工作环境满意度内部结构的相关结果分析
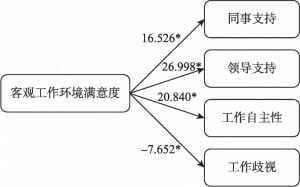
- 1.客观工作环境的结果分析
- 2.组织工作环境的结果分析
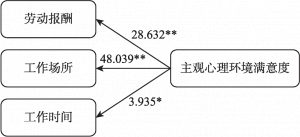
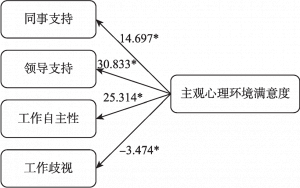
- 3.主观心理环境的结果分析
- (二)工作环境满意度内部结构的关系讨论
- 1.关系路径一:客观工作环境→组织工作环境
- 2.关系路径二:客观工作环境→主观心理环境
- 3.关系路径三:组织工作环境→主观心理环境
- (三)我国城镇居民工作环境满意度现状讨论
- 1.2015年城镇居民工作环境满意度较高,同比上升5.85分
- 2.城镇居民对客观工作环境的满意度总体较高,但加班现象仍然较为严重
- 3.城镇居民对组织工作环境的评价整体提升,但较弱的工作自主性影响了组织工作环境满意度
- 4.城镇居民的主观心理环境良好,但工作压力问题日益凸显
- (一)工作环境满意度内部结构的相关结果分析
-
五 城镇居民工作环境满意度的差异分析与讨论
- (一)人口学变量的影响结果分析
- 1.自然特征变量:性别/年龄/婚姻状况/民族/宗教信仰
- 2.社会特征变量:户口类型/收入水平/受教育程度
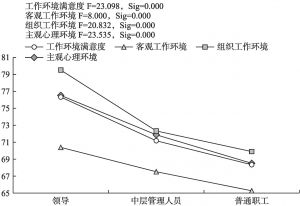
- 3.工作特征变量:单位类型/职位/社会保障机制
- (二)讨论
- 1.性别差异:加班现象显著出现于男性群体,工作歧视显著出现于女性群体
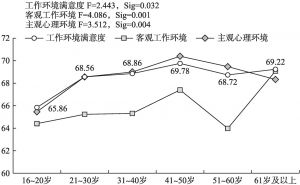
- 2.年龄差异:工作环境满意度在31~40岁上的最低点已消失,城镇居民对工作环境的满意度随年龄的增长呈波动上升趋势
- 3.户口差异:城镇化进程的带动使得农民工群体与城镇居民在工作环境满意度上已无显著差异,但工作自主性的缺失、年龄与性别歧视却显著存在于城镇居民群体中
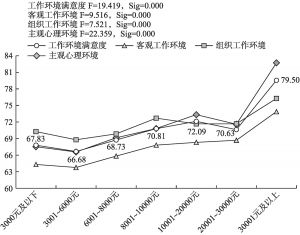
- 4.收入差异:家庭月收入为2万~3万元的中高收入城镇居民对工作环境的主观评价较低
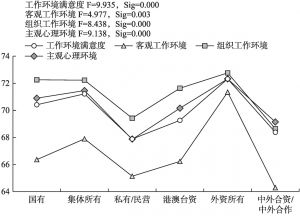
- 5.单位性质差异:港澳台资企业工作环境改善,外资企业工作环境满意度最高,而私有/民营企业的工作环境却仍不尽如人意
- (一)人口学变量的影响结果分析
-
六 城镇居民工作环境满意度的影响因素探讨
- (一)城镇居民工作环境满意度与社会满意度的关系
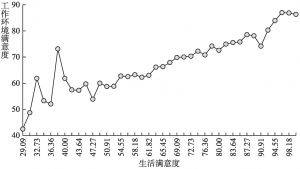
- (二)城镇居民工作环境满意度与生活满意度的关系
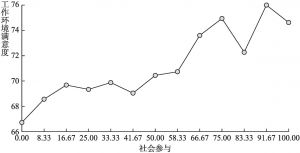
- (三)城镇居民的工作环境满意度与社会参与的关系
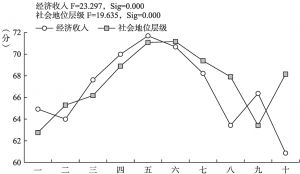
- (四)城镇居民的工作环境满意度与社会分层的关系
- 七 结论与思考
相关文献
查看更多>>>