章节
市场经济转型时期中国城市的规模和增长
摘要
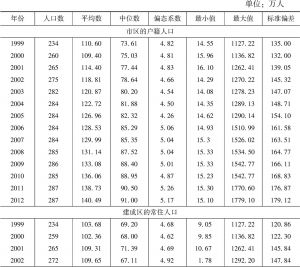
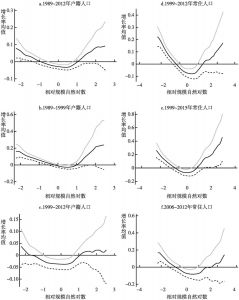
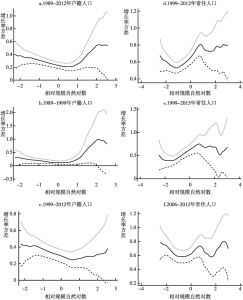
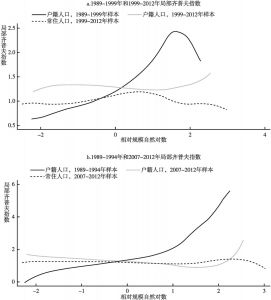
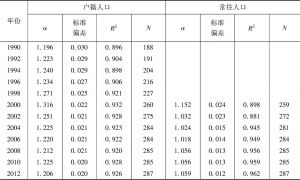
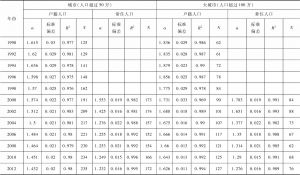
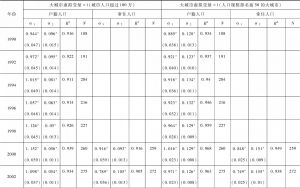
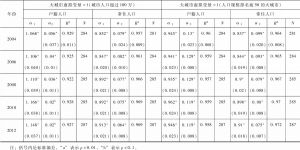
本文应用非参数方法研究与审视了中国城市的规模和增长。利用1989~2012年城市户籍人口数据以及1999~2012年城市常住人口数据,本文侧重于考察中国城市规模与城市增长速度之间的关系。不同规模城市增长率均值的核回归分析揭示了城市增长和规模之间的“U”形关系,否定了吉布拉定律。也就是说,大城市呈发散增长,而小城市呈收敛增长。分析结果还表明,如果采用城市常住人口数据而非户籍人口数据进行估计,大城市的增长会显得更加发散,而小城市的增长则显得没那么收敛。常住人口包括一部分流动人口,因此,可得出结论,从农村转移到大城市的人口比例失衡,使得大城市比小城市增长得更快。位序-规模(齐普夫)指数的OLS估计结果证明了大城市的发散增长,同时也否定了中国城市是遵循随机增长模式(这也获得了面板单位根检验的支持)。国家城市化战略强调对超级城市和特大城市的增长进行控制,本文的研究分析显示,这个战略过去并没有抑制特大城市的增长,未来的数十年内对中国城市化轨道可能仍然不产生显著影响。可持续城市化能否实现将在很大程度上取决于大城市是否准备好适应快速增长以及是否准备得充分。
关键词