论文
TFP and labor productivity: empirical facts of China’s macro-economy and issues for long-run economic growth
关键词
参考文献 查看全部 ↓
TFP and labor productivity: empirical facts of China’s macro-economy and issues for long-run economic growth
检索正文关键字
论文目录
-
1. Situation and problems of China’s macro-economy in 2013 and 2014
- 1.1. The three key demands
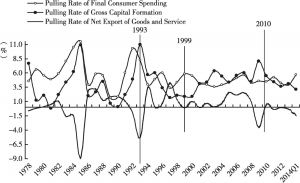
- 1.1.1. The total import and export trade volume of goods is approaching the boundary, reducing space for scale expansion
- 1.1.2. The boundary of investment rates appears and the problems with investment structure and investment efficiency become acute
- 1.1.3. There is a lack of endogenous mechanisms for consumption driven economic growth
- 1.2. Structure distortion and market risk
- 1.3. Predictions and outlook for 2014
- 1.1. The three key demands
-
2. Structural changes: growth trend of next five years (2014-2019)
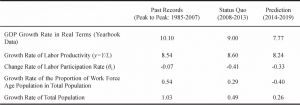
- 2.1. GDP growth decomposition: based on labor productivity and changes in demographic structure
- 2.1.1. Growth rate of total population and growth rate of demographic dividend
- 2.1.2. Change rate of labor participation rate
- 2.1.3. Growth rate of labor productivity
- 2.1.4. Scenario analysis of population change in economic growth
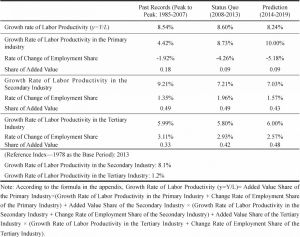
- 2.2. Decomposition of structural factors in labor productivity change: industrial allocation effect
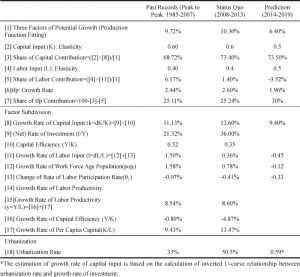
- 2.3. Estimation of potential growth rate: based on C-D production function and nonlinear dynamics of variables
- 2.3.1. Supply of labor force
- 2.3.2. Capital input
- 2.3.3. Long-term situation of factors’ elastic change
- 2.3.4. Total factor productivity
- 2.1. GDP growth decomposition: based on labor productivity and changes in demographic structure
-
3. Analysis of efficiency imbalance
- 3.1. Influences of labor force reallocation due to efficiency imbalance
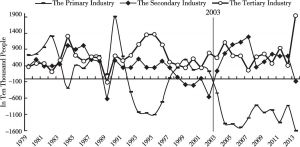
- 3.2. Slowdown and the imbalance of labor productivity
- 3.3. The change of TFP and its non-equilibrium: analysis based on city data
- 3.3.1. Average state of TFP growth of 264 cities across the nation
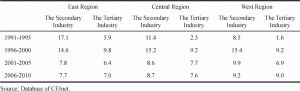
- 3.3.2. Regional TFP contrast
- 3.3.3. Correlation between GDP and TFP
-
4. The issue of efficiency compensation: efficient supply and transformation of economic growth mode
- 4.1. The raising of questions
- 4.2. The sequence of efficiency compensation
- 4.3. Investment efficiency compensation, consumption efficiency compensation and efficient supply
- 4.3.1. The first time efficiency compensation: analysis of investment efficiency compensation
- 4.3.2. The second time efficiency compensation: analysis of consumption efficiency compensation
- 4.3.3. Supplementary explanation of factor decomposition of growth and efficiency in Table 3 and Table 4
-
5. Policy suggestions
- 5.1. To transform the ideas on economic management
- 5.2. To attach importance to improving income distribution and fostering human capital
- 5.3. Re-understanding of the path of industrialization and urbanization of central and western regions
- Appendix: Formula derivation of whole-Society labor productivity growth rate
相关文献
of China’s current economic development pattern
agriculture management and administration system
effects in China: scale, structure, and its function in external adjustment
查看更多>>>