摘要
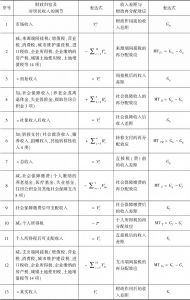
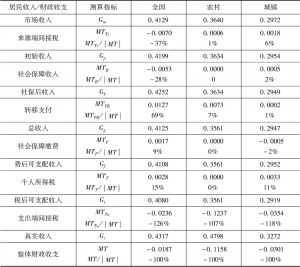
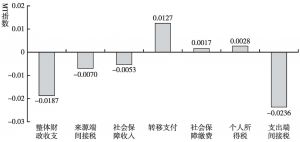
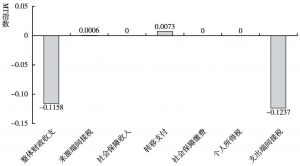
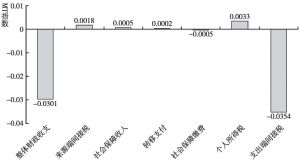
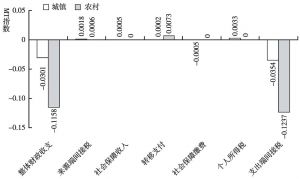
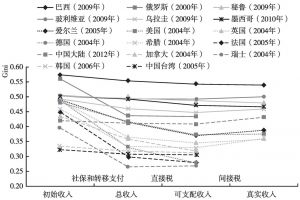
本文拓展了财政再分配的传统分析方法,将间接税纳入研究框架,从而构建一个可以综合测算包括各项税收、社会保障和转移支付在内的财政工具的再分配效应的分析框架。本文综合采用财政预算归宿法、居民收入核算框架法和MT指数测量与分解法,以中国2012年投入产出表和城乡居民调查数据为基础,构建了社会核算矩阵和可计算一般均衡模型,测算结果表明,我国的财政再分配从整体上对收入分配为逆向调节。Gini系数由财政作用前的0.4129上升为财政作用后的0.4316,上升幅度为4.5%;其中,来源端间接税的贡献为-37%,社会保障收入的贡献为-28%,转移支付的贡献为69%,社保缴费的贡献为9%,个人所得税的贡献为15%,使用端间接税的贡献为-126%。财政再分配还拉大了城乡收入分配差距。这一现象在中等收入国家和高收入国家中均不多见,主要原因在于,我国转移支付、社会保障支出、个人所得税和社会保障缴费在财政支出和收入中所占比重过低,对收入分配的正向调节力度过小,间接税在财政收入中占比过高,对收入分配的负向调节力度过大。
作者
娄峰 ,金融学博士,研究员,教授,博士生导师,中国社会科学院数量经济与技术经济研究所经济预测分析研究室主任,兼任中国系统工程学会社会经济系统专业委员会理事长,长期专注于宏观经济预测和政策模拟分析研究。出版《中国财政税收理论与政策模拟:基于CGE模型》等十多部专著;在《中国社会科学》《经济研究》《世界经济》《中国工业经济》《数量经济技术经济研究》等核心期刊发表论文数十篇;主持和参与数十项国家社科基金、国家自然基金、部委课题;获得部级一等奖3项、二等奖6项、三等奖10项,中国数量经济学年会一等奖2项。
- 金成武:《离散分布收入数据基尼系数的矩阵向量形式及相关问题》,《经济研究》2007年第4期。
- 李吉雄:《我国财政对居民收入再分配的绩效分析——基于贫困度和基尼系数的测度》,《经济问题》2010年第12期。
- 李实:《对基尼系数估算与分解的进一步说明——对陈宗胜教授评论的再答复》,《经济研究》2002年第5期。
- 米增渝、刘霞辉、刘穷志:《经济增长与收入不平等:财政均衡激励政策研究》,《经济研究》2012年第12期。
- 王传纶、高培勇:《当代西方财政经济理论》,商务印书馆,2002。
- 王延中、龙玉其、江翠萍、徐强:《中国社会保障收入再分配效应研究——以社会保险为例》,《经济研究》2016年第2期。
- 岳希明、张斌、徐静:《中国税制的收入分配效应测度》,《中国社会科学》2014年第6期。
- 赵永、王劲峰:《经济分析:CGE模型与应用》,中国经济出版社,2008。
- Aronson J.R.,Lambert P J.,“Decomposing the Gini Coefficient to Reveal the Vertical,Horizontal,and Reranking Effects of Income Taxation”,National Tax Journal,47(2).
- Bach Stefan,M. Grabka,and E. Tomasch,“Tax and Transfer System:Considerable Redistribution Mainly Via Social Insurance”,Diw Economic Bulletin,2015(8).
- Browning E.K.,“The Burden of Taxation”,The Journal of Political Economy,1978.
- Browning,Edgar K.,and William R. Johnson,“The Distribution of the Tax Burden”,Washington:American Enterprise Institute,1979.
- Caminada,Koen,K. Goudswaard and C. Wang,“Disentangling Income Inequality and the Redistributive Effect of Taxes and Transfers in 20 LIS Countries Over Time”,Mpra Paper,2012.
- Dalton,Hugh,Principles of Public Finance,4th ed.,New York Frederick A. Praeger,1955.
- Figari F.,“GINI DP 28:The impact of Indirect Taxes and Imputed Rent on Inequality:A Comparison with Cash Transfers and Direct Taxes in Five EU Countries”,Gini Discussion Papers,2012.
- Figari F.,Paulus A.,Sutherland H.,et al.,“Taxing Home Ownership:Distributional Effects of Including Net Imputed Rent in Taxable Income”,Social Science Electronic Publishing,2012.
- Gale,William G.,et al.,“Effects of After-Tax Pension and Social Security Benefits on Household Wealth:Evidence from a Sample of Retirees”,Social Science Electronic Publishing,2007.
- Goñi,Edwin,J. H. López and L. Servén,“Fiscal Redistribution and Income Inequality in Latin America”,Social Science Electronic Publishing,2008,39(9).
- Huesca L.,Araar A.,“Progressivity of Taxes and Transfers:The Mexican Case 2012”,Ssrn Electronic Journal,2014.
- Immervoll H.,Levy H.,Lietz C.,et al.,“Household Incomes and Redistribution in the European Union:Quantifying the Equalizing Properties of Taxes and Benefits”,Economics,2005.
- Kakwani N.C.,“Measurement of Tax Progressivity:An International Comparison”,Economic Journal,1977,87(345).
- Lustig N.,Gray-Molina G.,Higgins S.,et al.,“The Impact of Taxes and Social Spending on Inequality and Poverty in Argentina,Bolivia,Brazil,Mexico,and Peru:A Synthesis of Results”,Public Finance Review,2013,42(3).
- Lustig,Nora,“Fiscal Redistribution In Middle Income Countries:Brazil,Chile,Colombia,Indonesia,Mexico,Peru and South Africa”,Oecd Social Employment & Migration Working Papers,2015.
- Mookherjee D.,Shorrocks A.,“A Decomposition Analysis of the Trend in UK Income Inequality”,Economic Journal,1982,92(92).
- Musgrave R. A.,Thin T.,“Income Tax Progression,1929-48”,Journal of Political Economy,1948(6).
- Nanak Kakwani,“On the Measurement of Tax Progressivity and Redistributive Effect of Taxes with Applications to Horizontal and Vertical Equity”,Advances in Econometircs,JAI press Inc.,vol.,3,1984.
- Nanak Kakwani,Analyzing Redistribution Policies,A Study Using Australian Data,New York:Cambridge University Press,1986.
- Pechman J.A.,Okner B.A.,“Who Bears the Tax Burden?”,Journal of Finance,1974.
- Reynolds M.O.,Smolensky E.,Public Expenditures,Taxes,and the Distribution of Income:the United States,1950,1961,1970,Academic Press,1977.
- Higgins S.,Lustig N.,Ruble W.,et al.,“Comparing the Incidence of Taxes and Social Spending in Brazil and the United States”,Review of Income & Wealth,2015.
- Smolensky,By E.,W. Hoyt and S. Danziger,“A Critical Survey of Efforts to Measure Budget Incidence”,The Relevance of Public Finance for Policy-Making,Proceedings IIFP Congress,1987.
- Wang,Chen and K. Caminada,“Disentangling Income Inequality and the Redistributive Effect of Social Transfers and Taxes in 36 LIS Countries”,Ssrn Electronic Journal,2011.
- Whiteford,P.,“How Much Redistribution do Governments Achieve the Role of Cash Transfers and Household Taxes,Growing unequal:Income Distribution and Poverty in OECD Countries”,in OECD,Growing Unequal,Income Distribution and Poverty in OECD Countires,Paris,Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Develpoment,2008.
- Wilhelm Pfähler,“Redistributive Effect of Income Taxation:Decomposing Tax Base and Tax Rates Effects”,Bulletin of Economic Research,1990,42(2).