报告
作为文化品牌的创意城市
摘要
创意城市由何种要素构成?而人们又将如何了解这些要素?简而言之,创意城市不仅仅关乎城市的实力水平和商贸发展(“国际城市”并不等同于创意城市),也不仅仅关乎文化(文化可以是历史遗迹),更不仅限于城市中存在着多少创意与文化产业(城市需要创意场所、创意群体和相关职位)。当然,城市需要创意人群,因为这一群体能够在综合生产技能和消费者需求的基础上,使用数字媒介和社交网络激发创意、促进实验、鼓励多样化发展。本文将分别探讨不同的系统和价值观,正是这些系统和价值观的交汇及彼此间极富生产力的积极碰撞,确保了具有全球竞争力的城市能够保存创意能力。本文通过借鉴一项由澳大利亚研发的新型创意城市指数,致力于展现创意集群、创意服务和创意人群将如何为一座城市带来竞争优势。利用这种方法,任何规模的城市都可以对其创意产业做出评估,并制定相关政策,推行具体措施,以提高该城市作为“文化品牌”的知名度。
检索正文关键字
报告目录
- 一 城市及其复杂性
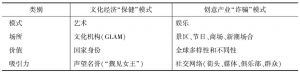
- 二 保健VS诈骗
- 三 创意城市
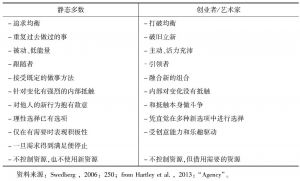
- 四 艺术家、消费者和系统碰撞:无名企业
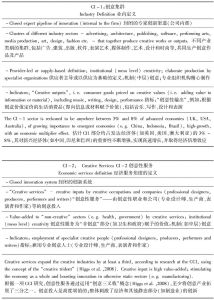
- 五 创意产业的四个阶段/模式
- 六 创造性破坏和社交学习
- 七 你准备怎么做?
- 八 作为文化品牌的创意城市
相关文献
查看更多>>>