论文
情绪表达矛盾一定会带来心理症状吗?文化规范的调节作用
摘要
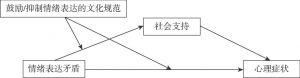
推崇“喜怒不形于色”的中国文化与鼓励“直抒胸臆”的西方文化会对“欲言又止”的心理症状造成不同的影响吗?本研究通过对来自美国(鼓励情绪表达的文化)与中国(抑制情绪表达的文化)的958份问卷的数据分析,揭示了抑制或鼓励情绪表达的文化规范在情绪表达矛盾与其后果变量的关系中所扮演的角色,证实了文化规范在其中的调节作用。具体而言,情绪表达矛盾导致问题心理症状增加和社会支持减少的结果仅出现在鼓励情绪表达的美国文化中,却没有出现在抑制情绪表达的中国文化中。有调节的中介模型进一步表明,文化规范调节了情绪表达矛盾与社会支持之间的关系——只有在美国文化中,情绪表达矛盾才因降低个体的社会支持而增加心理症状。最后,文章讨论了该研究未来的发展方向和研究局限。
作者
常保瑞 ,广西师范大学教育学部心理学系教授、博士生导师。
谢天 ,心理学博士,外国哲学博士后,武汉大学哲学学院心理学系副教授、硕士生导师。中国社会心理学会理事、中国心理学会社会心理学分会理事,中国社会心理学会文化心理学分会秘书长,Asian Journal of Social Psychology编委(2021~2023年)。从事社会心理学研究,主要研究方向为文化心理、决策与谈判心理等,主持和参与国内外及省部级项目多项。在国内核心期刊,如《心理学报》《心理科学》《心理科学进展》《应用心理学》等,以及国外SSCI期刊,如Journal of CrossCultural Psychology, Asian Journal of Social Psychology, Public Personnel Management等,以第一作者或通讯作者身份发表论文多篇。电子信箱:thanksky520@126.com
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 引言
-
二 文献回顾和研究假设
- (一)情绪表达矛盾与心理症状的关系
- (二)情绪表达矛盾、社会支持与心理症状的关系
- (三)鼓励/抑制情绪表达的文化规范作为边界条件
- 1.鼓励/抑制情绪表达的文化规范调节AEE与心理症状之间的关系
- 2.鼓励/抑制情绪表达的文化规范调节AEE与社会支持之间的关系
- (四)小结
-
三 方法
- (一)被试
- (二)研究工具
- 1.情绪表达矛盾问卷
- 2.社会支持量表
- 3.心理症状量表
- (三)研究思路
- (四)数据分析与处理
-
四 结果
- (一)共同方法偏差的控制与检验
- (二)各变量的描述统计与相关分析结果
- (三)社会支持在AEE和心理症状之间的中介作用
- (四)美中文化在AEE和心理症状关系中的调节作用
- (五)美中文化规范在AEE和社会支持关系中的调节作用
- (六)有调节的中介模型
-
五 讨论
- (一)研究小结
- (二)研究展望
- (三)实践启示
- (四)研究局限
- 六 结论
相关文献
查看更多>>>