论文
欧洲福利国家开支大紧缩:新型社会风险下社会投资取得的部分成功
摘要
当前,欧洲国家正面临福利开支大紧缩的问题(a“big squeeze”)。在资源受到限制的同时,已有的健康照护和养老金将需要更高的支出,其背后的原因是人口老龄化所带来的日渐增长的日常支出,以及预期值的日益提高。与此同时,年青一代也提出了新的需求,集中表现在三个领域:①促进相关儿童照顾、家庭友好型工作环境,以及反性别歧视的立法建设,从而保障妇女进入劳动力市场,获取平等工作机会;②由于技能和就业之间的联系更加密切,所以需要加强培训和就业支持,以提高就业质量;③在不平等加剧的社会背景下,为底层提供更多的福利和工资。相比为年轻人提供的服务,老年人所享受的服务开销更大,不过建立得还算完善,也受到选民的支持。给年轻人的福利资源投入却在不断缩减。2007年金融危机之后,紧随其后的经济停滞和开支紧缩加剧了资源投入的压力。在这种情况下,积极(activation)和社会投资型项目是非常有吸引力的,因为这些项目不仅支出少,而且会很有经济竞争力。这些项目通过儿童照顾、教育、培训和职业支持服务,帮助妇女和年轻人获得工作机会,并通过提高技能减少贫困。欧洲经验是,在应对性别和家庭问题时,社会投资项目表现出一定优势。中国目前也正经历着人口老龄化过程,为了应对各方面压力,刺激国内消费,社会支出也在不断增加,未来中国是否会发生和欧洲相似的问题我们还不得而知。如果我们的目标是在平等的框架下实现公平,那么就需要重新考虑积极政策的局限性。
作者
杨团 ,中国社会科学院社会学研究所研究员,中国社会科学院社会政策研究中心顾问,中国社会科学院研究生院教授、硕士生导师。曾任中国社会学会社会政策研究专业委员会理事长;现任中国灵山公益慈善促进会监事长、北京农禾之家咨询服务中心理事长、北京农禾之家农村发展基金会理事长等职。国家民政部特邀咨询专家,劳动与社会保障部社会保障专家组成员。获评“2013CCTV年度十大慈善人物”“责任中国2014年公益盛典”年度致敬大奖,《中国慈善家》杂志“2015年度中国十大社会推动者”“2018年度中国十大社会推动者”“2020年度十大公益人物”,《南风窗》杂志2018年“为了公共利益年度人物”。2019年获评“中国慈善公益品牌70年70人”代表人物。2021年进入“2021中国品牌女性500强”,获评凤凰网行动者联盟2021十大公益人物奖。担任《当代社会政策研究》(社会政策专业委员会学术年会暨社会政策国际论坛年度论文集2005~2017)和《中国慈善发展报告》(2009~2022)的主编;《综合农协:中国“三农”改革突破口》(北京农禾之家咨询服务中心综合农协研究组年度研究报告论文集2013~2021)的主编主撰。长期致力于社会保障、慈善公益与非营利组织、综合性农民合作组织、社区公共服务、老年人长期照护等领域的政策研究,曾多次主持国家社科基金课题和重点课题以及中国社科院重点课题,出版多部专著、发表150多篇论文及研究报告,曾获国家社科基金优秀成果及多项省部级研究优秀成果奖。主要专著有《社区公共服务论析》(独著)、《中国社会保障制度的再选择》(第一著者)、《21世纪中国农民的社会保障之路》(第一著者);主要论文有《社会政策研究范式的演化及其启示》《新农村建设与农村社会保障探索》《探索第四域》《医疗卫生服务体系改革的第三条道路》《中国长期照护的政策选择》《此集体非彼集体——为社区性综合性乡村合作组织探路》《30年集体经济改革启示录:乡村发展必由之路》等。
房莉杰 ,毕业于中国人民大学社会学系,获社会学博士学位。现任中国社会科学院社会学研究所社会政策室副主任、研究员,中国社会科学院社会政策研究中心副主任,联合国发展研究所(UNRISD)合作研究员。主要研究领域是卫生政策、长期照护、社会政策模式。出版独著《新型农村合作医疗制度信任的形成过程》、合著《老年长期照护的国际经验》,在《社会学研究》等学术期刊发表论文二十余篇。
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 背景:不同的欧洲福利国家对于公平的不同观念
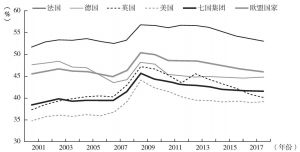
- 二 欧洲福利国家的最新挑战:新老社会风险并存
- 三 回应:社会福利政策改革的两个方案
-
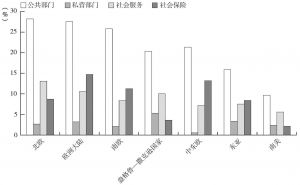
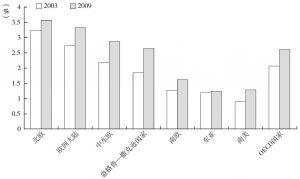
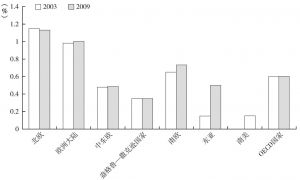
四 新型社会政策的影响:福利开支的“大紧缩”
- 社会投资
- 积极的社会政策/社会投资:政策结果
- 总体评价
-
五 对理论和实践的影响:以欧洲和中国为例
- 社会政策的理论发展
- 政策方向
相关文献
查看更多>>>