章节
全球生产网络下珠海制造业创新能力提升与参与全球中高端竞争对策研究
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 一 引言
- 二 全球生产网络下企业创新能力形成的机制
-
三 全球生产网络下影响企业创新能力的因素
- 1.企业的研发支出水平
- 2.企业规模
- 3.外向性程度
- 4.多元化程度
- 5.所有权特征
- 6.信贷约束
- 7.人力资本投资
- 8.税收激励政策
- 9.财政补贴政策
-
四 实证分析
- (一)建立量化指标
- (二)数据预处理
- 1.全要素生产率的计算
- 2.模型初步建立
- (三)数据分析
- 1.数据的描述性统计
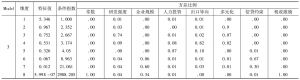
- 2.变量的相关性分析
- 3.初步回归分析
- 4.修正模型
-
五 政策建议
- (一)影响珠海制造业创新能力因素与全国比较
- (二)提升珠海制造企业创新能力,参与全球中高端竞争的对策
查看更多>>>