章节
交易制度、投资者结构与股票市场波动
摘要
交易制度设计的合理性与股价波动率之间存在密切关系。本文综合比较A股市场、中国台湾市场与美国、中国香港市场的波动率,从宏观层面初步证明实施涨跌停制度并没有让市场变得更加稳定。基于AH股的微观分析发现,涨跌停制度是A股市场个股股价高波动率的重要原因;在实施涨跌停制的A股市场,融资融券制度的引入在现阶段也加剧了股价波动。熔断机制与涨跌停制度虽然在目标上有共同点,但两项制度的作用机制存在差异,如果同时实施则会产生冲突。促进中国股市健康发展,需要进一步完善交易制度,让市场发挥决定性作用;注重监管协调,更好地发挥政府作用;重视对大户投资者交易行为的监管;严厉打击违法交易行为,建立公开、公正、公平的市场环境。
作者
王朝阳 ,男,江苏连云港人,经济学博士,中国社会科学院财经战略研究院《财贸经济》编辑部主任、副研究员、硕士生导师。2002年毕业于山东大学经济学院金融系,获经济学学士学位;2004年、2007年毕业于中国社会科学院研究生院财贸经济系,分别获经济学硕士和博士学位。2007年7月—2009年2月,在财政与贸易经济研究所服务经济理论与政策研究室,任助理研究员;2009年2月起任中国社会科学院财经战略研究院(原财政与贸易经济研究所)《财贸经济》编辑部副主任,2012年2月起兼任《专报》(内部资料)编辑室副主任并主持工作。2013年3月以来任中国社会科学院研究生院硕士生导师。研究领域为宏观经济与金融体制改革、服务经济理论与政策等。主持国家社会科学基金课题、中国社会科学院国情调研课题,参与多项国家社会科学基金重大课题、国家自然科学基金课题,主持和参与国家开发银行、中国保险保障基金公司等单位多项委托课题。在《经济研究》《中国工业经济》《世界经济》《经济学动态》《求是》以及ChinaFinanceandEconomicReview等期刊发表论文40余篇,出版学术著作《金融服务产业集群研究:兼论中国区域金融中心建设》、译著《服务业的生产率、创新与知识:新经济与社会经济方法》等,主编《中国金融服务理论前沿(6)》《中国服务经济理论前沿(1)》等。
王振霞 ,经济学博士,副研究员,中国社会科学院财经战略研究院研究室主任,主要研究方向为宏观经济学、价格理论。
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 一 引言
-
二 文献综述与研究假设
- (一)相关文献评述
- (二)研究框架与基本假设
-
三 研究设计及数据说明
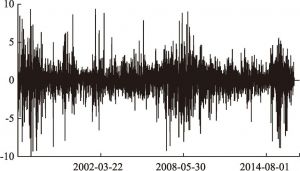
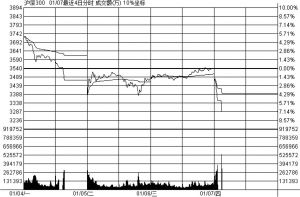
- (一)涨跌停制度与股市波动率的直观比较
- (二)基于AH股的股价波动率影响因素
- (三)引入融资融券制度后的进一步讨论
- (四)A股市场交易者结构对股市波动率的影响
- (五)变量定义及数据来源
-
四 实证结果及分析
- (一)基于不同股票市场波动率差异的直观比较
- (二)基于AH股的股价波动率影响因素
- (三)引入融资融券交易后的进一步分析
- (四)投资者结构与市场波动率的关系
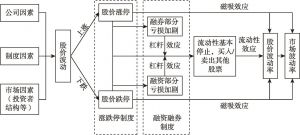
- 五 熔断机制与涨跌停制度的兼容性分析
-
六 结论与建议
- (一)以市场化为原则,逐步稳妥推进改革
- (二)注重监管协调,更好地发挥政府作用
- (三)高度重视对大户交易者的行为监管
- (四)严厉打击违法交易行为,建立公开、公正、公平的市场环境
相关文献
查看更多>>>