论文
患者社会地位感知与对医信任:差别性的影响因素
摘要
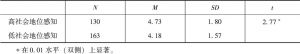
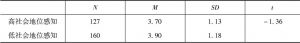
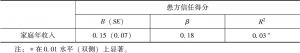
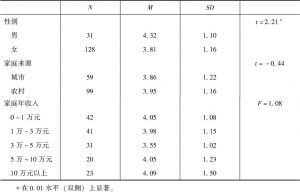
个体社会地位高低的认知与患者对医信任是否存在某种关系?又受到何种因素的影响?本研究选取300名过去一年内自己或家属曾有就诊经历的被试,启动其社会地位感知后考察对医信任的水平。结果显示,社会地位感知与患方对医信任不存在相关关系。相关分析和回归分析显示,家庭年收入对高社会地位感知组患方的对医信任有显著的正向影响(β=0.18,p<0.05),能够有效解释高地位感知组对医信任得分变异的3%。差异检验结果显示,低地位感知组患方信任具有显著的性别差异,男生显著高于女生[t(1,158)=2.21,p<0.05]。研究结论:社会地位感知与患方对医信任不存在相关关系,高低社会感知组对医信任的影响因素是有差别的:高地位感知组对医信任的影响因素是家庭经济收入,低社会感知组对医信任的影响因素是性别。
作者
朱艳丽 ,郑州大学教育学院心理学系讲师,硕士生导师。
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 前言
-
二 方法
- (一)被试
- (二)工具
- 1.社会地位感知的启动和操控
- 2.社会地位感知量表
- 3.患者对医信任问卷
- (三)统计方法
-
三 结果
- (一)社会地位感知启动效应检验
- (二)社会地位感知与患方对医信任的关系
- (三)社会地位感知分组对医信任得分差异性分析
- (四)高社会地位感知组对医信任影响因素的分析
- (五)低社会地位感知组对医信任影响因素的分析
-
四 讨论
- (一)社会地位感知与患方对医信任不存在相关关系
- (二)高社会地位感知组对医信任的影响因素:家庭经济收入
- (三)低社会地位感知组对医信任的影响因素:性别
相关文献
查看更多>>>