论文
不平等与经济增长
摘要
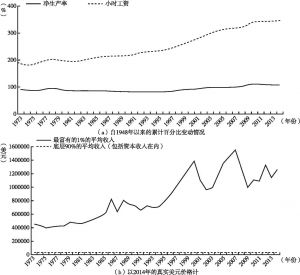
无论是从收入不平等、财富不平等,还是从机会不平等角度看,美国的不平等问题都很严重,并呈现不断加剧的趋势。不平等问题也正在全球众多国家蔓延。相比而言,美国已经变成全球发达经济体中最不平等的国家。为不平等辩护的边际生产率理论,存在严重的缺陷。收入分配不能为标准的经济学理论所解释。不平等的代价是巨大而且多元的。不断加剧的不平等是富裕国家当下的经济困境的重要原因。在过去的35年里,最富裕的国家发展演变的三个显著特征是财富与收入比例的增加、工资中位数的停滞和资本回报率下降的失灵。通过更好的公司治理、反垄断和反歧视的法律、一个被更好地监管的金融体系、更健全的工人权利、更激进的税收和转移支付政策等来“重写治理市场经济的规则”,一个更平等的、更强劲的经济增长是可能实现的。
作者
斯蒂格利茨 (Joseph Stiglitz),哥伦比亚大学校级讲座教授、哥伦比亚大学政策对话倡议组织(Initiative for Policy Dialogue)主席
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 引言
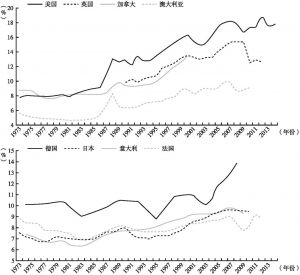
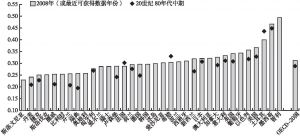
- 二 不平等的大幅加剧
- 三 普遍化的国际趋势
- 四 解释不平等
- 五 寻租和顶层群体收入
- 六 租金的增加
- 七 制度和政治的作用
- 八 不平等的代价
- 九 逆转不平等
- 十 小结:重新定义经济增长
查看更多>>>