章节
会计稳健性、信息不对称与并购绩效
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 一 引言
-
二 理论分析与研究假设
- 1. 会计稳健性能够抑制管理者向上操纵盈余等机会主义行为
- 2.会计稳健性可以及时地反应“坏消息”,并及时地确认损失
- 3. 会计稳健性可以获取更多关键资源的支持
-
三 研究设计
- 1.样本和数据来源
- 2.变量测量与说明
-
四 实证结果与分析
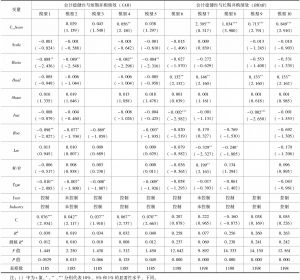
- 1.会计稳健性对并购绩效影响的实证结果
- 2.会计稳健性降低信息不对称的实证结果
- 3.稳健性检验
- 五 结论与启示
相关文献
查看更多>>>