章节
西部地区人才引进政策能够促进企业创新吗?
摘要
人才是社会经济发展的第一资源、第一动能。当前我国西部地区人才匮乏问题仍很突出,难以适应促进区域协调发展的目标要求。本文从企业创新的视角考察在经济相对落后的西部地区,高层次人才引进政策如何有效落地。研究发现,高层次人才引进政策对西部地区企业创新具有显著的促进作用。进一步研究表明,政府“高层次人才引进政策”中涉及“常驻支持”、“个人发展”及“经费支持”的激励措施对企业创新具有显著的促进作用。当政策着力于消除人才的后顾之忧、将人才个人发展与地区经济发展相结合,并为人才提供配套科研资金支持时,人才对企业创新会产生持续促进作用。此外,随着西部各个地市经济发展水平、教育人文环境、居住环境和市场化程度等制度环境因素的优化,人才引进政策对企业创新的促进作用日益显著。本文将为政府制定合理政策消除西部地区人才困境、促进区域技术进步和经济高质量发展提供参考。
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 一 引言
-
二 制度背景和研究假设
- (一)制度背景
- (二)文献综述与研究假设
-
三 研究设计
- (一)样本选取与数据来源
- (二)模型设计
- (三)变量定义
- 1.企业创新
- 2.西部人才引进政策
- 3.控制变量
- (四)描述性统计
-
四 实证结果与分析
- (一)西部人才引进政策与企业创新
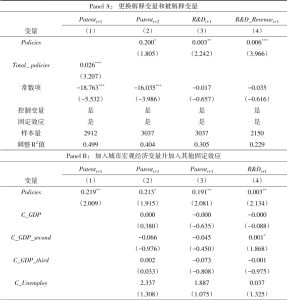
- (二)高层次人才引进政策如何将人才留在西部地区?
-
五 稳健性检验
- (一)缓解潜在的内生性问题
- 1.平行趋势检验
- 2.安慰剂测试
- 3.邻近市匹配
- 4.PSM匹配
- (二)其他稳健性检验
- (三)排除其他相关政策影响
- (一)缓解潜在的内生性问题
-
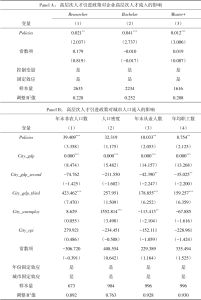
六 异质性检验和机制检验
- (一)异质性检验
- (二)机制检验
- 七 结论
相关文献
查看更多>>>