章节
通向新增长的路径:人力资本、创新和技术变迁的驱动力量
关键词
作者
〔澳〕江诗伦(Lauren Johnston) 感谢杨晟朗在搜集本章所使用数据时提供的帮助。
宋立刚 ,澳大利亚国立大学克劳福德(Crawford)公共政策学院教授,博士生导师,中国人民大学经济学院讲座教授。
蔡昉 ,中国社会科学院国家高端智库首席专家、学部委员,中国人民银行货币政策委员会委员,中国社会科学院原副院长,中国非洲研究院原院长,第十一、十二、十三届全国人民代表大会常务委员会委员,第十三届全国人民代表大会农业与农村委员会副主任委员。主要研究领域为中国经济改革和发展、人口经济学、劳动经济学、经济增长、收入分配和减贫等。著有《人口负增长时代:中国经济增长的挑战与机遇》《中国经济发展的世界意义》《中国经济增长展望:从人口红利到改革红利》等。近年获中国出版政府奖、中华人口奖、孙冶方经济科学奖、张培刚发展经济学优秀成果奖、中国发展百人奖、中国农村发展研究奖等。
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 引言
-
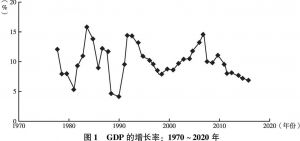
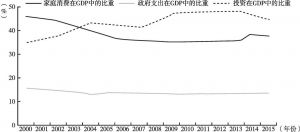
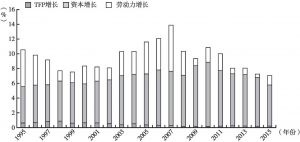
宏观经济发展
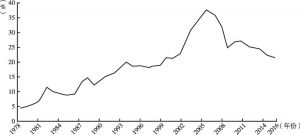
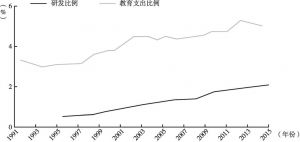
- 人力资本
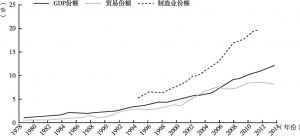
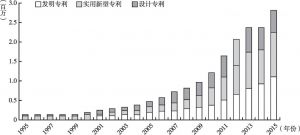
- 创新和技术
-
本书的结构
- 第一部分:改革与宏观经济发展
- 第二部分:教育与人力资本
- 第三部分:创新与生产率
- 第四部分:部门技术变迁
- 第五部分:技术与贸易、投资
查看更多>>>