论文
“一带一路”背景下边疆基础设施的增长效应估计
摘要
从近年来国家发布的重要文件来看,如何在国家“一带一路”战略背景下建设边疆逐渐成为政界、学界十分重视的议题。本文通过使用边疆地区九省区的省级面板数据和地市级面板数据,主要探讨铁路建设与公路建设是否拉动了边疆地区的经济增长,估计结果如下。第一,铁路建设的经济效应与公路建设的经济效应存在一定替代性,20世纪90年代以后,公路的影响越来越小,而铁路的影响越来越大。第二,铁路的增长效应有明显的异质性,以京哈铁路与沈大铁路为例,京哈铁路的通车对沿线城市的经济起到促进作用,而沈大铁路的通车却对沿线城市的经济起到了负面作用。第三,影响机制。京哈铁路的通车之所以有正向影响,是因为该铁路线连通了东北地区与北京,使得两地的要素流动更加便利,且铁路通车主要是通过影响固定资产投资来促进经济的;沈大铁路的通车之所以是负面的,在于该线没有出东北区域,且该线的通车使得东北地区的人口流动性更强,可能是因为沈大铁路的通车加速了东北地区的人口流出,进而对东北地区经济起到了负面作用。本文的结论对于今后边疆铁路建设与公路建设的区位布局,有一定参考价值。
作者
检索正文关键字
论文目录
-
1 研究背景
- 1.1 边疆建设的政治要求与边疆基础设施建设的重要性
- 1.2 新常态经济增长降速与“一带一路”战略
- 1.3 边疆基础设施建设如何对接“一带一路”战略
-
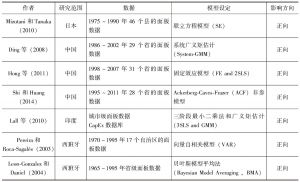
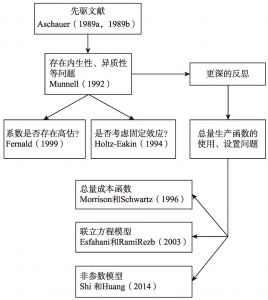
2 文献综述
- 2.1 研究方法的演进过程
- 2.2 基础设施对经济增长的影响方向及国别差异
- 2.3 基础设施回报率的估计值跨度较大
-
3 研究方法和数据说明
- 3.1 研究思路和方法
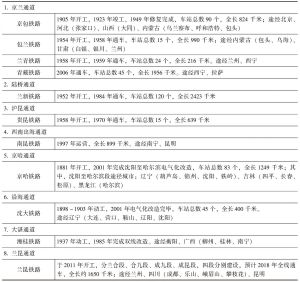
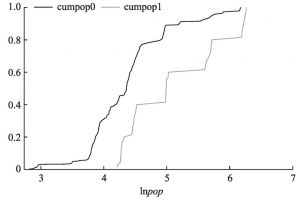
- 3.2 数据说明
-
4 实证分析与结果
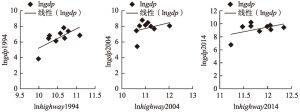
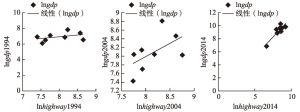
- 4.1 相关性分析
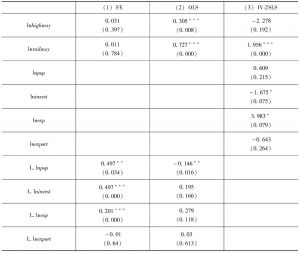
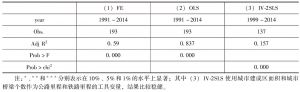
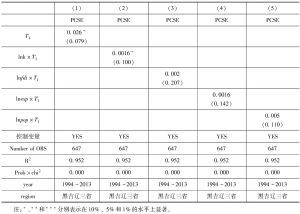
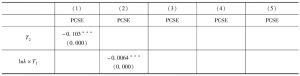
- 4.2 基于省际面板数据的回归结果
- 4.3 基于地市级面板数据的回归结果
- 5 分析结论
相关文献
查看更多>>>