论文
强弱关系,还是关系人的特征同质性
摘要
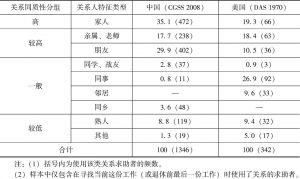
梳理社会网络和社会资本研究领域涉及弱关系与强关系命题的争论发现,尽管各自阵营的讨论都可以逻辑自洽,可本文的探讨说明,以找工作讨论为例,强、弱关系或许只是表象,让强、弱关系发生作用的不是关系强、弱本身,而是关系人在社会特征属性上的同质性。运用DAS数据和CGSS数据的分析表明,无论在美国还是中国,曾经被解释为在找工作中发生影响的弱关系或强关系,在更本质的意义上是关系人的特征同质性,关系强弱在多大程度上发挥影响,取决于关系人在社会特征属性上的同质性程度。
作者
邱泽奇 ,湖北沔阳(今仙桃)人,北京大学社会学系教授,教育部“长江学者奖励计划”特聘教授,北京大学社会学系学术委员会主任,北京大学中国社会与发展研究中心主任,北京大学数字治理研究中心主任;主要研究方向为数字社会与治理、组织变迁、社会研究方法、城乡社会学等。代表性成果有《重构关系:数字社交的本质》《中国人的习惯》《朋友在先——中国对乌干达卫生发展援助案例研究》《边区企业的发展历程》等著作,以及《技术与组织:多学科研究格局与社会学关注》《技术化社会治理的异步困境》《从数字鸿沟到红利差异——互联网资本的视角》《回到连通性——社会网络研究的历史转向》《技术与组织的互构——以信息技术在制造企业的应用为例》等论文。
乔天宇 ,北京大学大数据分析与应用技术国家工程实验室博士后;研究方向为技术社会学、组织社会学、计算社会学。
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 在找工作中,关系强弱真的重要吗?
-
二 关系强弱之争
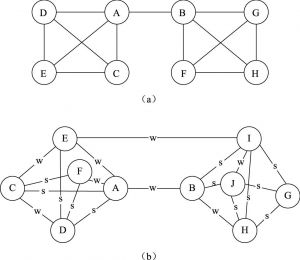
- (一)弱关系:桥、捷径与结构洞
- (二)强关系:中国事实?
- (三)被忽略的:关系人的社会特征属性
-
三 回到同质性
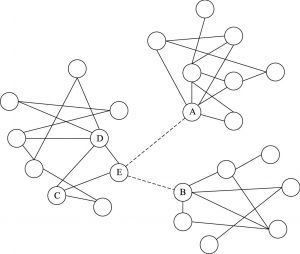
- (一)同质性现象
- (二)关系人的特征同质性与研究假设
- (三)数据、变量与分析方法
-
四 特征同质性与关系强度
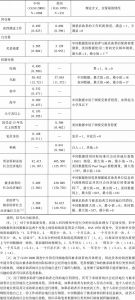
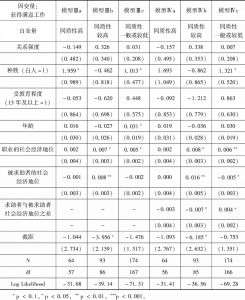
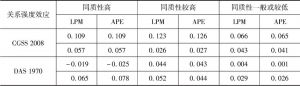
- (一)来自中国调查数据的证据
- (二)关系人的特征同质性假设在美国社会同样有效吗?
- 五 结论
相关文献
查看更多>>>