章节
锂离子电池性能衰退机理与故障预警策略研究
摘要
本文基于新能源汽车用锂离子动力电池在车载复杂工况下由于老化过程造成整车性能下降以及产生安全隐患的问题开展研究,首先分析锂离子电池老化机理,研究老化路径对衰减过程的影响;其次对当前常用的电池模型方法进行了总结,并着重介绍了动力电池电化学-热-机耦合仿真模型;再次分析了实际应用下锂离子电池伴随老化过程可能出现的风险,归纳了主要容量衰退分析方法;最后阐明了基于动力电池云端控制的故障预警方案将是动力电池整车应用未来的发展方向。
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 一 绪论
-
二 锂离子电池老化机理研究
- (一)温度影响
- 1.高温环境影响
- 2.低温环境影响
- (二)充放电倍率与循环次数
- (三)SOC影响及放电区间
- (一)温度影响
-
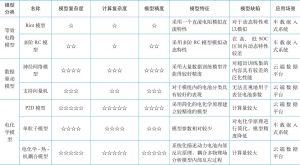
三 锂离子电池建模方法
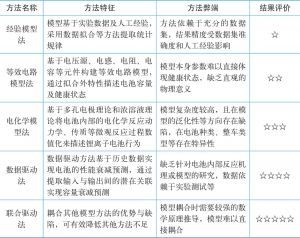
- (一)锂离子电池等效模型
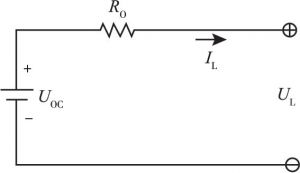
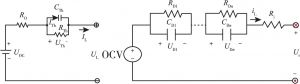
- 1.等效电路模型
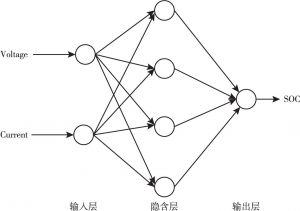
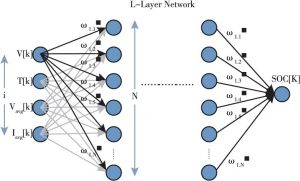
- 2.数据驱动模型
- 3.电化学模型
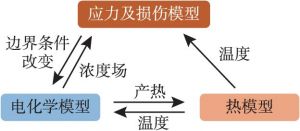
- (二)电化学-热-机耦合模型在动力电池老化中的应用
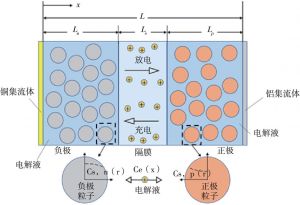
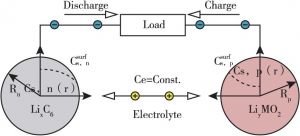
- 1.P2D模型
- 2.热模型
- 3.机械模型
- (三)仿真模型在大数据应用环境下的改进
- (一)锂离子电池等效模型
-
四 电池故障预警策略优化研究
- (一)衰退引发的安全性风险
- 1.热稳定性下降导致的风险
- 2.容量不一致性导致的风险
- (二)容量衰退识别方法
- 1.基于模型驱动的方法
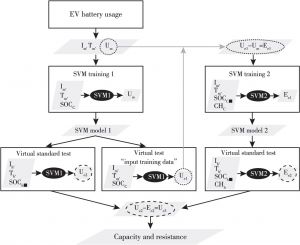
- 2.数据驱动方法
- 3.联合驱动方法
- (三)基于云端模型分析的故障预警方案
- 1.动力电池实际工况研究
- 2.基于大数据的时变工况提取
- 3.云端预警模型建立
- (一)衰退引发的安全性风险
- 五 结论
查看更多>>>