论文
分析师关注的盈余管理治理作用
摘要
分析师的外部治理对证券市场的有效运行有重要意义,有研究指出分析师的外部治理存在局限性,本文针对此问题,从分析师声誉机制、企业内部环境改善两个渠道探讨了加强分析师外部治理有效性的可能。实证结果显示,我国证券市场分析师关注能够抑制企业应计盈余管理,但刺激更隐蔽的真实盈余管理;单纯通过分析师声誉机制不能缓解盈余管理问题,明星分析师关注会强化企业以真实盈余管理替代应计盈余管理的倾向;而内部环境改善有利于该问题的解决,它通过降低关注成本等机制发挥影响,在内部控制达到特定水平后,分析师关注将减少真实盈余管理而不是刺激真实盈余管理,这意味着企业内部控制与分析师外部治理存在协同效应。
作者
左志刚 ,男,广东外语外贸大学会计学院教授。
石方志 ,女,安永华明会计师事务所深圳分所。
Zhigang Zuo
Fangzhi Shi
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一、引言
-
二、文献综述
- (一)分析师关注对盈余管理的外部治理效应
- 1.分析师外部治理效应的产生
- 2.分析师关注对企业盈余管理的治理效应
- (二)影响分析师外部治理作用的相关因素
- 1.分析师声誉
- 2.企业内部控制质量
- (一)分析师关注对盈余管理的外部治理效应
-
三、理论分析与研究假设的提出
- (一)分析师关注与企业盈余管理的基本关系
- (二)分析师声誉与分析师外部治理作用的有效性
- (三)企业内部控制质量与分析师外部治理作用的有效性
-
四、研究设计
- (一)模型设定
- (二)变量设计
- 1.因变量
- 2.解释变量
- 3.控制变量
- (三)样本与数据来源
-
五、实证结果分析
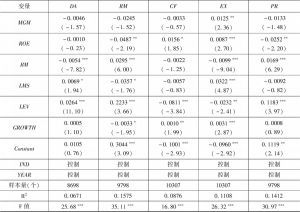
- (一)描述性统计结果
- (二)分组盈余管理差异
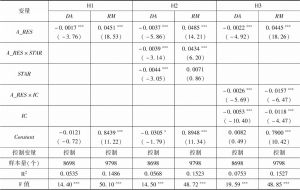
- (三)回归结果分析
- 1.分析师关注与盈余管理的基本关系
- 2.分析师声誉的调节作用
- 3.内部控制质量的调节作用
-
六、稳健性检验
- (一)剔除分析师关注对象选择偏好后的回归
- (二)使用工具变量的回归
- 七、结论
相关文献
查看更多>>>