论文
The Moderating Role of Perceptions of Organizational Politics on the Relationship between Paternalistic Leadership and Employee Silence
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 1 Introduction
-
2 Literature Review and Hypotheses Building
- 2.1 Paternalistic leadership
- 2.2 Paternalistic leadership and employee silence
- 2.3 The moderating role of perceptions of organizational politics
-
3 Research Methods
- 3.1 Sampling
- 3.2 Variable measurement
-
4 Empirical Results
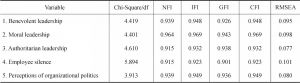
- 4.1 Reliability and validity analysis
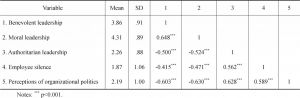
- 4.2 Descriptive analysis
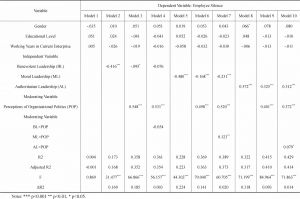
- 4.3 Regression analysis
-
5 Discussions and Conclusions
- 5.1 Paternalistic leadership: the adverse and facilitating effects of employee silence
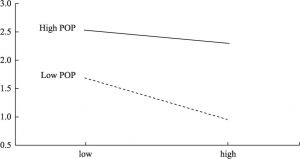
- 5.2 Perceptions of organizational politics: environmental perception moder-ates the leadership effectiveness
- 5.3 Managerial implications
- 5.4 Limitations and future research
相关文献
Study on the Binary Option Pricing Formula with Regime-Switching
Exploring Factors Affecting Expenditures on Media
Regulation of Executive Compensation of SOEs: Empirical Evidence from China Stock Market
A Psychographic Study of the Formation Mechanism of Green Purchase Intention among Chinese Consumers
A Study on the Models of Monetary Policy in China
The Economic Growth Model Based on Entrepreneurship Capital
Financial Vulnerability, Inflation and Economic Development in China
Studies on the Pattern of Short-Term Fluctuations in China’s Business Cycles
查看更多>>>