章节
真实进步指标测算结果及比较分析
检索正文关键字
章节目录
-
6.1 测算结果与分析
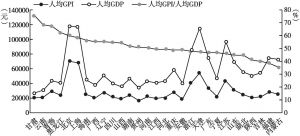
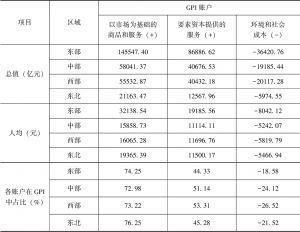
- 6.1.1 全国GPI、人均GPI
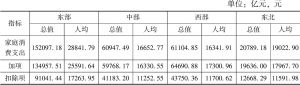
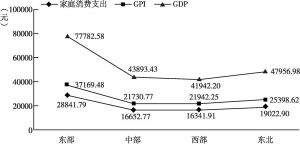
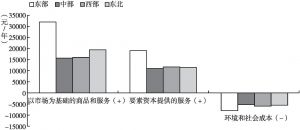
- 6.1.2 东、中、西及东北区域GPI、人均GPI测算结果与分析
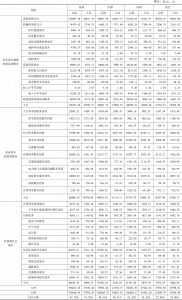
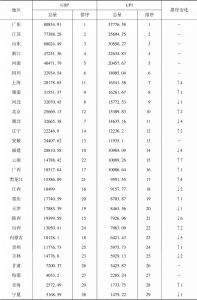
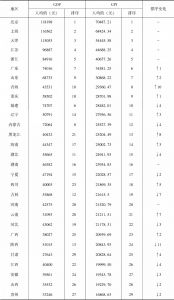
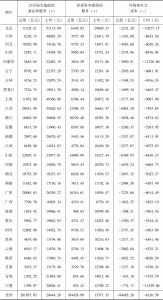
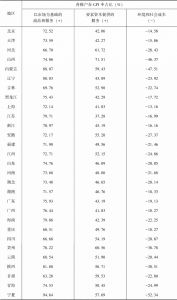
- 6.1.3 各地区GPI、人均GPI测算结果与分析
-
6.2 三大账户比较
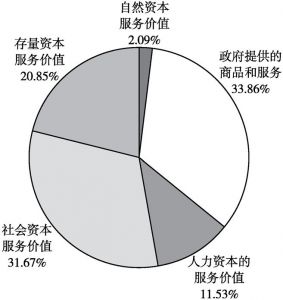
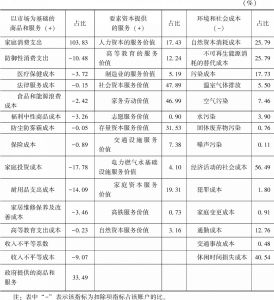
- 6.2.1 全国GPI各账户比较
- 1.各账户间的比较
- 2.各账户内的比较
- 6.2.2 区域GPI各账户比较
- 1.各账户间的比较
- 2.各账户内的比较
- 6.2.3 地区GPI各账户比较
- 1.各账户间的比较
- 2.各账户内的比较
- 6.2.1 全国GPI各账户比较
-
6.3 GPI的国内外比较
- 6.3.1 国家GPI比较
- 6.3.2 国家GPI/GDP比较
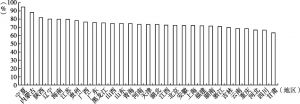
- 6.3.3 地区GPI比较
- 6.3.4 地区GPI/GDP比较
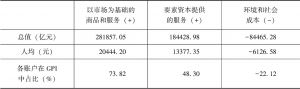
- 6.3.5 和中国现有GPI测算结果比较
- 6.3.5.1 人均GPI对比
- 6.3.5.2 GPI/GDP对比
查看更多>>>