论文
群体本质主义与群际刻板印象:自然类别和群体实体性如何预测热情和能力?
摘要
以往研究发现群体本质主义增强群际刻板印象,并对群际关系具有负面作用。但这些研究多采用单一维度界定群体本质主义。本研究从群体本质主义包含自然类别和群体实体性的两维度视角出发,结合刻板印象内容模型,用两个研究考察群体本质主义与群际刻板印象的关系。研究1发现群体的自然类别和群体实体性对热情均有显著的负向预测作用,研究2发现对于不同的群体,个体对其自然类别和群体实体性的知觉与对其能力和热情的知觉之间的关系也不同。最后,就群体本质主义的两维结构、刻板印象内容模型所定义的群体刻板印象,以及两者之间的关系进行了讨论。
作者
韦庆旺 ,中国人民大学心理学系、国家民委民族语言文化心理重点研究基地、教育部民族教育发展中心民族心理与教育重点研究基地副教授,硕士生导师
董文兰 ,中国人民大学心理学系硕士生
武心丹 ,北京市建华实验学校教师,通信作者,E-mail:spurscherry@126.com。
周欣彤 ,中国人民大学心理学系硕士生。
唐楠棋 ,北京大学心理与认知科学学院硕士生。
Wei Qingwang
Dong Wenlan
Wu Xindan
Zhou Xintong
Tang Nanqi
参考文献 查看全部 ↓
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 引言
-
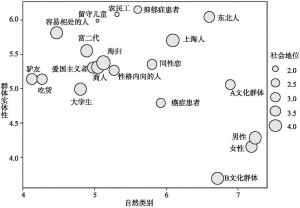
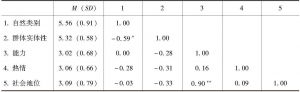
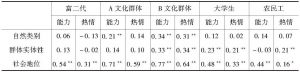
二 研究1:社会代表性群体的本质主义与刻板印象知觉
- (一)方法
- 1.被试
- 2.测量
- (二)结果和讨论
- (一)方法
-
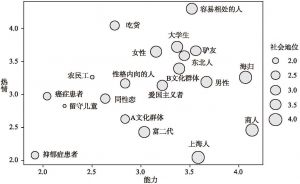
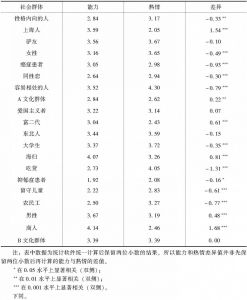
三 研究2:聚焦5个群体考察本质主义与刻板印象的关系
- (一)方法
- 1.被试
- 2.测量
- (二)结果和讨论
- (一)方法
- 四 总体讨论
查看更多>>>