论文
网络平台对食品安全风险进行管控的博弈机制研究
摘要
新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情发生以来,许多消费者会选择通过网络平台采购食品,同样地,食品制造企业也会越来越多地通过网络平台进行销售。网络平台不仅能够利用在线评论通过大数据分析为制造商提供更多更精准的市场需求信息,同时也有能力担负起对食品安全风险进行管控的责任。本文首先构建了基于食品制造企业与网络平台企业的两层供应链模型,其次通过斯塔克伯格博弈,分析当食品制造企业和网络平台分别占据市场主导地位时的两种供应链情境,得到制造商最优产品质量和网络平台最优食品监管水平的策略。最后,通过一系列的仿真实验得到一些管理启示:第一,食品制造企业有寻找监管水平低的网络平台进行销售的动机,但是食品制造企业想要获得最大收益还是需要提升“内功”,老老实实做好产品质量。第二,当食品制造企业占主导地位时,本身产品质量过硬、声誉好的制造商会拿走网络平台的大多数利润,而当网络平台占主导地位时,网络平台也会有选择中小型食品加工企业为其生产自有品牌产品的可能。第三,网络平台能够利用产品在线评价信息、用户画像、基于地理信息的推送服务等大数据分析手段了解消费市场需求,对食品安全风险进行有效管控,最终能够为其自身和制造商带来双赢。
作者
王嘉馨 ,中国美术学院中国画与书法艺术学院助理研究员,研究方向为公共关系、媒介研究;
傅啸 ,杭州电子科技大学浙江省信息化发展研究院副教授,研究方向为供应链企业信任关系、食品安全供应链;
韩广华 ,上海交通大学国际与公共事务学院副教授,研究方向为食品安全、风险治理。
Wang Jiaxin
Fu Xiao
Han Guanghua
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 引言
- 二 文献综述
- 三 模型设计
-
四 模型分析
- (一)食品制造企业占主导
- (二)网络平台占主导
- (三)两者同等地位
-
五 数值分析
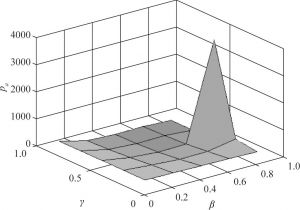
- (一)食品制造商占主导的实例分析
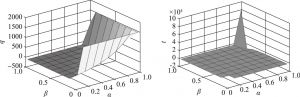
- 1.当确定时,、与、之间的关系
- 2.当确定时,、与、之间的关系
- 3.当确定时,、与、之间的关系
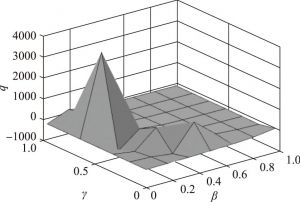
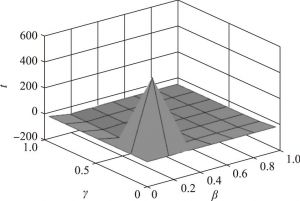
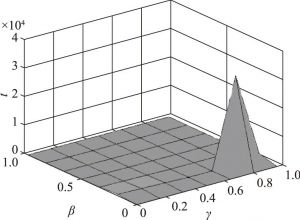
- (二)网络平台占主导地位的实例分析
- 1.当确定时,、与、之间的关系
- 2.当确定时,、与、之间的关系
- 3.当确定时,、与、之间的关系
- (一)食品制造商占主导的实例分析
- 六 结论
查看更多>>>