摘要
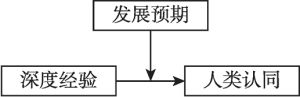
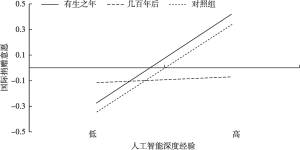
人工智能正在成为人类共同的外群体对象,它比动物更智能、比外星人更现实,随着技术的发展普及而随处可见。那么使用人工智能会提升“我是人类中一员”的认同感吗?发展预期在其中起何作用?本研究考察人工智能深度经验与人类认同的关系,以及发展预期的调节作用。结果显示,人工智能深度经验与人类认同倾向、国际捐赠意愿显著正相关,且发展预期在其中起显著调节作用,即当发展预期较乐观时,人工智能深度经验正向预测人类认同倾向、国际捐赠意愿;当发展预期较悲观时,上述预测效应不再显著。结果表明,人工智能的深度使用有助于提升人类认同,尤其当大众对人工智能发展抱乐观预期时,可能会促进人类命运共同体的积极构建。
作者
王从余 ,中国人民公安大学讲师,清华大学社会科学学院博士。
翟崑 ,北京大学国际关系学院国际政治系教授、博士生导师;北京大学区域与国别研究院副院长、全球互联互通研究中心主任。主要研究领域为东南亚、亚太问题,世界政治与国际战略问题,以及中国的国际化战略、“一带一路”等。曾任中国现代国际关系研究院世界政治研究所所长(2011~2014)、南亚东南亚及大洋洲研究所所长(2008~2011),研究员。长期从事全球、周边地区及国别的综合研究和科研管理。东盟地区论坛(ARF)中方专家名人、中国东南亚研究会副会长、中国外交学会理事,以及泛北部湾经济合作中方专家组成员、中国-东盟博览会高级顾问。
彭凯平 ,清华大学社会科学学院心理学系教授,博士生导师。
- 管健、荣杨,2020,《共同内群体认同:建构包摄水平更高的上位认同》,《西北师大学报》(社会科学版)第1期。
- 王从余,2021,《人工智能觉知影响人类认同》,博士学位论文,清华大学。
- 温忠麟、叶宝娟,2014,《中介效应分析:方法和模型发展》,《心理科学进展》第5期。
- Abrams,D. & Hogg,M.(1990). An Introduction to the Social Identity Approach. In(pp.1-9).
- Adams,S.,Arel,I.,Bach,J.,Coop,R.,Furlan,R.,Goertzel,B.,…& Schlesinger,M.(2012). Mapping the landscape of Human-level Artificial General Intelligence. AI magazine,33(1),25-42.
- Bartneck,C.,Kulic′,D.,Croft,E. & Zoghbi,S.(2009). Measurement Instruments for the Anthropomorphism,Animacy,Likeability,Perceived Intelligence,and Perceived Safety of Robots. International Journal of Social Robotics,1(1),71-81.
- Baum,J.,Buddington,A.,Johnson,H.,Sampson,E. & Smith,B.(1957). GUI-DEBOOK FOR FIELD TRIPS. Paper Presented at the Guidebook for Field Trips:Atlantic City Meeting,1957.
- Beni,G. & Wang,J.(1993). Swarm Intelligence in Cellular Robotic Systems. In Robots and Biological Systems:Towards a New Bionics?(pp.703-712):Springer.
- Benoît,M.,Thierry,L.,Olivier,G. & Harold,M.(2012). Behavioral Investigation of the Influence of Social Categorization on Empathy for Pain:A Minimal Group Paradigm Study. Frontiers in Psychology,3,389.
- Bonato,M.,Zorzi,M. & Umiltà,C.(2012). When Time is Space:Evidence for a Mental Time Line. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews,36(10),2257-2273.
- Brown,R.(2020). TheOrigins of the Minimal Group Paradigm. History of Psychology,23(4),371-382.
- Brown,T.,Mann,B.,Ryder,N.,Subbiah,M.,Kaplan,J.,Dhariwal,P.,…& Amodei,D.(2020). Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. In Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems,Vancouver,Canada.
- Cerda,C. & Warnell,K.R.(2020). Young Children’s Willingness to Deceive Shows in-group Bias only in Specific Social Contexts. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology,198.
- Dick,R.V.,Wagner,U.,Stellmacher,J. & Christ,O.(2005). Category Salience and Organizational Identification. Journal of Occupational & Organizational Psychology,78(2).
- Duffy,B.R.(2003). Anthropomorphism and the Social Robot. Robotics and Autonomous Systems,42(3),177-190.
- Dunham,Y.(2018). Mere Membership. Trends in Cognitive Sciences,22(9),780-793.
- Gaertner,S.L.,Dovidio,J.F.,Anastasio,P.A.,Bachman,B. & Rust,M.C.(1993). The Common Ingroup Identity Model:Recategorization and the Reduction of Intergroup Bias. European Review of Social Psychology,4(1),1-26.
- Gaertner,S.L.,Dovidio,J.F. & Bachman,B.A.(1996). Revisiting the Contact Hypothesis:The Induction of a Common Ingroup Identity. International Journal of Intercultural Relations,20(3),271-290.
- Gaertner,S.L. & Dovidio,J.F.(2005). Understanding and Addressing Contemporary Racism:From Aversive Racism to the Common Ingroup Identity Model. Journal of Social Issues,61.
- Gamez-Djokic,M. & Waytz,A.(2020). Concerns About Automation and Negative Sentiment Toward Immigration. Psychological science,31(8),987-1000.
- Goertzel,B.(2014). Artificial General Intelligence:Concept,State of the Art,and Future Prospects. Journal of Artificial General Intelligence,5(1),1.
- Grace,K.,Salvatier,J.,Dafoe,A.,Zhang,B. & Evans,O.(2018). When will AI Exceed Human Performance?Evidence from AI Experts. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research,62,729-754.
- Greischel,H.,Noack,P. & Neyer,F.J.(2018). Oh,the Places You’ll go!How International Mobility Challenges Identity Development in Adolescence. Developmental Psychology,54(11),2152-2165.
- Hayes,A.F.(2013). Model Templates for PROCESS for SPSS and SAS. Retrieved from www.guilford.com/p/hayes3.
- Hertel,G. & Kerr,N.L.(2001). Priming In-Group Favoritism:The Impact of Normative Scripts in the Minimal Group Paradigm. Journal of experimental social psychology,37(4),316-324.
- Hewstone,M.,Rubin,M. & Willis,H.(2002). Intergroup bias. Annual review of psychology,53(1),575-604.
- Higgins,E.(1996). Knowledge activation:Accessibility,Applicability,and Salience. Social Psychology:Handbook of basic Principles.
- Hinkle,S. & Brown,R.(1990). Intergroup Comparisons and Social Identity:Some Links and Lacunae. In D.E.Abrams & M.A.Hogg(Eds.),Social Identity Theory:Constructive and Critical Advances(pp.70). London:Pearson Education Limited.
- Hogg,M.A.(2000). Social Identity and Social Comparison. In Handbook of Social Comparison(pp.401-421):Springer.
- Hogg,M.A.(2016). Social Identity Theory. In S.McKeown,R.Haji,& N.Ferguson(Eds.),Understanding Peace and Conflict Through Social Identity Theory(pp.3-17). Switzerland:Springer,Cham.
- IEEE Spectrum.(2017,May). Human-level AI is right around the corner—or hundreds of years away. https://spectrum.ieee.org/humanlevel-ai-is-right-around-the-corner-or-hundreds-of-years-away#RodneyBrooks.
- Iliadis,L.,Maglogiannis,I.,Papadopoulos,H.,Karatzas,K. & Sioutas,S.(2012). Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations(Vol.381):Springer.
- Jackson,J.C.,Castelo,N. & Gray,K.(2019). Could a Rising Robot Workforce Make Humans Less Prejudiced?American Psychologist,75(7).
- Kile,F.(2013). Artificial Intelligence and Society:A Furtive Transformation. AI & SOCIETY,28(1),107-115.
- Kirby,C.R.(2019). Expertise,Ethos,and Ethics:The Prophetic Rhetoric of Nick Bostrom and Elon Musk in the Artificial Intelligence Debate.(Ph.D.). Wake Forest University,
- Long,L.N.(2017). Toward Human-Level(and Beyond)Artificial Intelligence. Presented at PSU Math Dept.
- Lucci,S. & Kopec,D.(2015). Artificial intelligence in the 21st century:Stylus Publishing,LLC.
- McCarthy,J.,Minsky,M.L.,Rochester,N. & Shannon,C.E.(2006). A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence,august 31,1955. AI magazine,27(4),12-12.
- McFarland,S.,Hackett,J.,Hamer,K.,Katzarska-Miller,I.,Malsch,A.,Reese,G. & Reysen,S.(2019). Global Human Identification and Citizenship:A Review of Psychological Studies. Political Psychology,40,141-171.
- McFarland,S.,Webb,M. & Brown,D.(2012). All Humanity is my Ingroup:A Measure and Studies of Identification with all Humanity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,103(5),830-853.
- Müller,V.C. & Bostrom,N.(2016). Future Progress in Artificial Intelligence:A Survey of Expert Opinion. In V.C.Müller(Eds.),Fundamental issues of artificial intelligence(pp.553-571). Berlin:Springer.
- Otten,S. & Mummendey,A.(1999). To our Benefit or at your Expense?Justice Considerations in Intergroup Allocations of Positive and Negative Resources. Social Justice Research,12(1),19-38.
- Otten,S.(2016). The Minimal Group Paradigm and its Maximal Impact in Research on Social Categorization. Current Opinion in Psychology,11,85-89.
- Plötner,M.,Over,H.,Carpenter,M. & Tomasello,M.(2015). The Effects of Collaboration and Minimal-group Membership on Children’s Prosocial Behavior,Liking,Affiliation,and Trust. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology,139,161-173.
- Richter,N.,Over,H. & Dunham,Y.(2016). The Effects of Minimal Group Membership on Young Preschoolers’ Social Preferences,Estimates of Similarity,and Behavioral Attribution. Collabra,2(1),8.
- Ross,L. & Nisbett,R.E.(2011). The Person and the Situation:Perspectives of Social Psychology(pp.34-35). London:Pinter & Martin Publishers.
- Russell,S. & Norvig,P.(2010). Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach,3rd Edition(M.Horton Ed.). Upper Saddle River,New Jersey:Pearson.
- Sanders,C.R.(1990). The Animal ‘other’:Self definition,Social Identity and Companion Animals. Advances in Consumer Research. Association for Consumer Research(U.S.),17(1),662-668.
- Silver,D.,Huang,A.,Maddison,C.J.,Guez,A.,Sifre,L.,Van Den Driessche,G.,… & Lanctot,M.(2016). Mastering the Game of Go with Deep Neural Networks and Tree Search. Nature,529(7587),484-489.
- Sparks,E.,Schinkel,M.G. & Moore,C.(2017). Affiliation Affects Generosity in Young Children:The Roles of Minimal Group Membership and Shared Interests. J Exp Child Psychol,159,242-262.
- SPECTRUM,I.(2017). Human-level AI is Right around the Corner-or Hundreds of Years Away. Retrieved from https://spectrum.ieee.org/humanlevel-ai-is-right-around-the-corner-or-hundreds-of-years-away#GaryMarcus.
- Tajfel,H.,Billig,M.G.,Bundy,R.P. & Flament,C.(1971). Social Categorization and Intergroup Behaviour. European Journal of Social Psychology,1(2),149-178.
- Tajfel,H. & Turner,J.C.(2010). An Integrative Theory of Intergroup Conflict. In T.Postmes & N.R.Branscombe(Eds.),Rediscovering Social Identity.(pp.173-190). New York,NY,US:Psychology Press.
- Turner,J.C.,Hogg,M.A.,Oakes,P.J.,Reicher,S.D. & Wetherell,M.S.(1987). Rediscovering the Social Group:A Self-categorization Theory:Basil Blackwell.
- Turner,J.C. & Oakes,P.J.(1986). The Significance of the Social Identity Concept for Social Psychology with Reference to Individualism,Interactionism and Social Influence. British journal of Social Psychology,25(3),237-252.
- Turner,J.C. & Onorato,R.S.(1999). Social Identity,Personality,and the Self-concept:A Self-categorizing Perspective. In The psychology of the Social Self.(pp.11-46). Mahwah,NJ,US:Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
- Vezzali,L.,Cadamuro,A.,Versari,A.,Giovannini,D. & Trifiletti,E.(2015). Feeling like a Group after a Natural Disaster:Common in-group Identity and Relations with Outgroup Victims among Majority and Minority young Children. British journal of Social Psychology,54(3),519.
- Walton,D.(2010). Appeal to Expert Opinion:Arguments from Authority:Penn State Press.
- Wang,P.(2019). On Defining Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Artificial General Intelligence,10(2),1-37.
- Weger,U.W. & Pratt,J.(2008). Time Flies like an Arrow:Space-time Compatibility Effects Suggest the Use of a Mental Timeline. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review,15(2),426-430.
- Wissing,B.G. & Reinhard,M.A.(2018). Individual differences in risk perception of artificial intelligence. Swiss Journal of Psychology,77(4),149-171.
- Yamagishi,T.,Mifune,N.,Liu,J.H. & Pauling,J.(2010). Exchanges of Group-based favours:Ingroup Bias in the Prisoner’s Dilemma Game with Minimal Groups in Japan and New Zealand. Asian Journal of Social Psychology,11(3),196-207.