论文
Reinforcement Learning in Repeated Portfolio Decisions
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 1 Introduction
-
2 The Reinforcement Learning Models
- 2.1 Basic Reinforcement Learning Model
- 2.2 Reinforcement Learning Representing Return,Risk,and Correlation
-
3 Experiment No.1
- 3.1 Method
- Participants
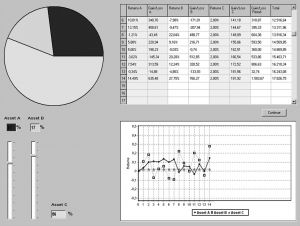
- Procedure
- 3.2 Results
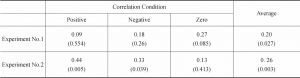
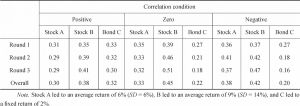
- 1.Risk attitude
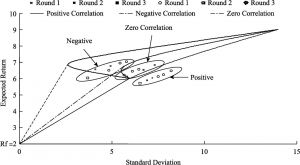
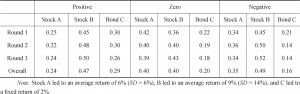
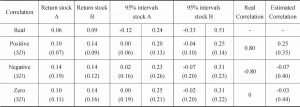
- 2.The MV model’s prediction and investment decisions
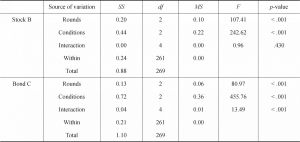
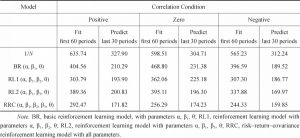
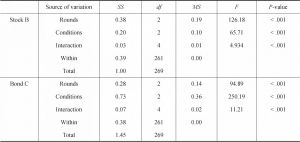
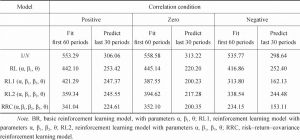
- 3.The learning models
- 3.3 Summary of Experiment No.1
- 3.1 Method
-
4 Experiment No.2
- 4.1 Methods
- 1.Participants
- 2.Procedure
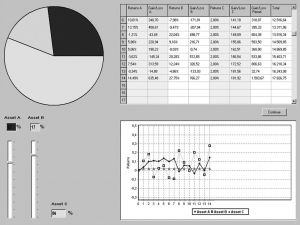
- 4.2 Results
- 1.Risk attitude
- 2.Comparison with the MV model’s prediction
- 3.Comparison of the two experiments
- 4.The learning models
- 4.2 Summary of Experiment No.2
- 4.1 Methods
- 5 General Discussion
-
Appendix (Not for publication)
- Instructions for Experiment No.1
- Part I Portfolio Decision Making
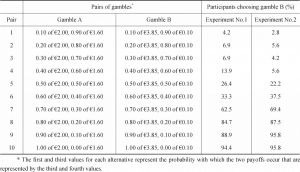
- Part II Gamble Choices
相关文献
The Driving Effect of Environmental Responsibility on Green Consumption Behavior in China
A Research on the Method of Fine Granularity Webpage Data Extraction of Open Access Journals
Education Promote or Hinder Job Mobility?
The Impact of Comparability of Accounting Information on M&A Target Selection
查看更多>>>