摘要
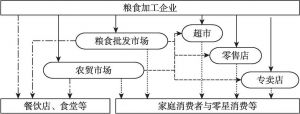
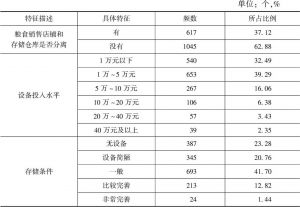
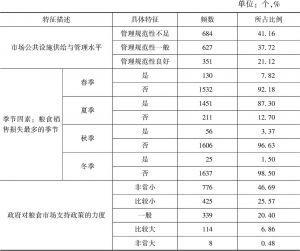
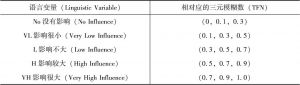
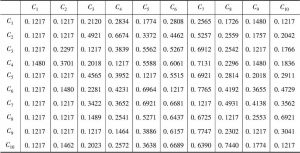
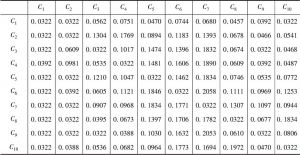
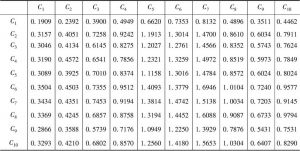
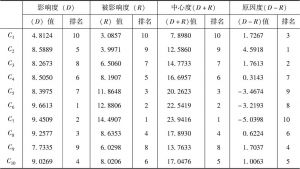
对人口众多、资源刚性约束大、“产前”和“产中”要素投入边际效应逐步下降的中国而言,“产后”的节粮减损具有重要的价值。销售作为粮食“产后”的最后环节在节粮减损上具有重要地位。本文以中国9省份51个地区1662个粮食销售商为实证研究对象,调查分析并归纳了可能影响销售商在销售环节粮食损失的主要因素,并应用基于模糊集理论的决策实验和评价实验法,依靠专家群体的参与,系统地分析了影响销售商在销售环节粮食损失因素间的相互关系,并识别了关键影响因素。研究结果表明,粮食销售商的年龄、设备投入水平、粮食存储条件、市场公共设施供给与管理水平、政府对粮食市场支持政策的力度是影响销售环节粮食损失的五个关键因素,并据此提出了政策建议。
作者
山丽杰 ,江南大学商学院硕士生导师,江苏省食品安全研究基地教授,研究方向为食品安全管理。
陈秀娟 ,江南大学食品安全风险治理研究院副研究员,主要从事食品安全治理等方面的研究。
臧秋霞
吴林海 ,江南大学商学院国际经济与贸易系教授。研究方向是食品安全风险治理。
- [1]Parfitt J.,Barthel M.,Macnaughton S.,“Food Waste within Food Supply Chains:Quantification and Potential for Change to 2050,” Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London,2010,365(1554):3065-3081.
- [2]Stuart T.,“Waste:Uncovering the Global Food Scandal,” Tenki,2009,56:971-981.
- [3]Gustavsson J.,Cederberg C.,Sonesson U. et al.,“Global Food Losses and Food Waste:Extent,Causes and Prevention,” FAO,2011.
- [4]郭燕枝、陈娆、郭静利:《我国粮食从“田间到餐桌”全产业链损耗分析及对策》,《农业经济》2014年第1期。
- [5]宋洪远、张恒春、李婕等:《中国粮食产后损失问题研究——以河南省小麦为例》,《华中农业大学学报》(社会科学版)2015年第4期。
- [6]吴林海、胡其鹏、朱淀等:《水稻收获损失主要影响因素的实证分析——基于有序多分类Logistic模型》,《中国农村观察》2015年第6期。
- [7]Unep N.,“Food Loss Prevention in Perishable Crops,” Pnuma,1981.
- [8]Vaclav Smil,“Improving Efficiency and Reducing Waste in Our Food System,” Environmental Sciences,2004,1(1):17-26.
- [9]Priefer C.,Jorissen J.,Brautigam K. R.,“Technology Options for Feeding 10 Billion People:Options for Cutting Food Waste,” European Parliament:Science and Technology Options Assessment,2013.
- [10]Peter Senker,“Foresight:The Future of Food and Farming,Final Project Report,” Prometheus,2011,29:309-313.
- [11]Aulakh J.,Regmi A.,Post-Harvest Food Losses Estimation-Development of Consistent Methodology,Agricultural & Applied Economics Association’s 2013 AAEA & CAES Joint Annual Meeting,Washington,D.C.,2013.
- [12]Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sicences,Postharvest Development Research Center,“Grain Post-production System Analysis in China:Terminal Report,”1991.
- [13]曹宝明:《粮食产后损失的测定与评价方法》,《南京经济学院学报》1997年第1期。
- [14]Teshome A.,Torrance J. K.,Baum B. et al.,“Traditional Farmers’ Knowledge of Sorghum [Sorghum Bicolor] (Poaceae) Landrace Storability in Ethiopia,” Economic Botany,1999,53(1):69-78.
- [15]赵霞、曹宝明、赵莲莲:《粮食产后损失浪费评价指标体系研究》,《粮食科技与经济》2015年第3期。
- [16]Eriksson M.,Strid I.,Hansson P. A.,“Food Losses in Six Swedish Retail Stores:Wastage of Fruit and Vegetables in Relation to Quantities Delivered,” Resources Conservation & Recycling,2012,68(6):14-20.
- [17]Stenmarck A.,Hanssen O. J.,Silvennoinen K.et al.,“Initiatives on Prevention of Food Waste in the Retail and Whole Sale Trades,” Copenhagen,Denmark:Nordic Council of Ministers,2011.
- [18]Mena C.,Adenso-Diaz B.,Yurt O.,“The Causes of Food Waste in the Supplier-retailer Interface:Evidences from the UK and Spain,” Resources Conservation & Recycling,2011,55(6):648-658.
- [19]Eriksson M.,Strid I.,“Food Loss in the Retail Sector:A Study of Food Waste in Six Grocery Stores,” Uppsala,Sweden:Swedish University of Agricultural Science,2011.
- [20]Grona K.,Sila Kamelerna,“En Miljoanalys av Coop Konsum,Stockholm,” Sweden:Coop Konsum,1995.
- [21]Buzby J. C.,Hyman J.,Total and Per Capita Value of Food Loss in the United States(Objectivity,Invariance,and Convention:Harvard University Press,2012):561-570.
- [22]Gjerris M.,Gaiani S.,“Household Food Waste in Nordic Countries.:Estimations and Ethical Implications,” Etikk I Praksis,2013,7(1):6-23.
- [23]Lebersorger S.,Schneider F.,“Food Loss Rates at the Food Retail,Influencing Factors and Reasons as a Basis for Waste Prevention Measures,” Waste Management,2014,34(11):1911-1919.
- [24]Kaminski J.,Christiaensen L.,“Post-harvest Loss in Sub-Saharan Africa:What Do Farmers Say?” Global Food Security,2014,3(3-4):149-158.
- [25]Kitinoja L.,Saran S.,Roy S. K. et al.,“Postharvest Technology for Developing Countries:Challenges and Opportunities in Research,Outreach and Advocacy,” Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2011,91(4).
- [26]Premanandh J.,“Factors Affecting Food Security and Contribution of Modern Technologies in Food Sustainability,” Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture,2011,91(15):2707-2714.
- [27]Koester U.,“Food Loss and Waste as an Economic and Policy Problem,” Intereconomics,2015,49(6):348-354.
- [28]安西友、刘长荣、曹东杰等:《平房仓粮食出入库过程中机械设备管理的探讨》,《粮食与食品工业》2012年第4期。
- [29]秦富、李先德、吕新业等:《河南小麦产业链各环节成本收益研究》,《农业经济问题》2008年第5期。
- [30]Mishra A.,Prabuthas P.,Mishra H. N.,“Grain Storage:Methods and Measurements,” Quality Assurance & Safety of Crops & Foods,2012,4(3):144-144.
- [31]Munesue Y.,Masui T.,Fushima T.,“The Effects of Reducing Food Losses and Food Waste on Global Food Insecurity,Natural Resources,and Greenhouse Gas Emissions,” Environmental Economics & Policy Studies,2015,17(1):43-77.
- [32]Boxall R. A.,“A Critical Review of the Methodology for Assessing Farm-level Grain Losses after Harvest,” International Biodeterioration,1986,25(4):318-319.
- [33]Papargyropoulou E.,Lozano R.,Steinberger J. K. et al.,“The Food Waste Hierarchy as a Framework for the Management of Food Surplus and Food Waste,” Journal of Cleaner Production,2014,76(4):106-115.
- [34]Thyberg K. L.,Tonjes D. J.,“Drivers of Food Waste and Their Implications for Sustainable Policy Development,” Resources Conservation & Recycling,2016,106(January 2016):110-123.
- [35]Gabus A.,Fontela E.,World Problems,an Invitation to Further Thought within the Framework of Dematel,ed.,Battelle Geneva Research Centre,Switzerland,Geneva,1972.
- [36]Gabus A.,Fontela E.,Perceptions of the World Problem Matique:Communication Procedure,Communicating with Those Bearing Collective Responsibility,ed.,Battelle Geneva Research Centre,Switzerland,Geneva,1973.
- [37]Herrera F.,Herrera-Viedma E.,MartíNez L.,“A Fusion Approach for Managing Multi-granularity Linguistic Term Sets in Decision Making,” Fuzzy Sets & Systems,2000,114(1):43-58.
- [38]Chiu Y. J.,Chen H. C.,Tzeng G. H. et al.,“Marketing Strategy Based on Customer Behavior for the LCD-TV,” International Journal of Management & Decision Making,2017,7(7):143-165.
- [39]Zadeh L. A.,“Fuzzy Sets,” Information & Control,1965,8(3):338-353.
- [40]Bellman R. E.,Zadeh L. A.,“Decision-Making in a Fuzzy Environment,” Management Science,1970,17(4):B141-B164.
- [41]Altrock C. V.,“Fuzzy Logic and Neuro Fuzzy Applications in Business and Finance,” Prentice-Hall,Inc.,1997.
- [42]Opricovic S.,Tzeng G. H.,“Compromise Solution by MCDM Methods:A Comparative Analysis of Vikor and Topsis,” European Journal of Operational Research,2007,156(2):445-455.