章节
财政政策的顺周期实施效应特征与基本成因
摘要
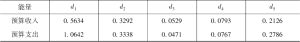
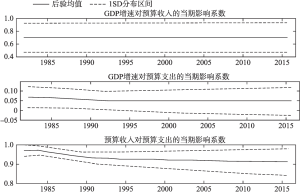
改革开放以来,为抵御外部风险、稳定经济增长,我国持续施用积极财政政策,政策设计愈发重视反周期相机调控理念。但政策的实施效果存在争议、不完全满足反周期特征,导致调控结果与初衷存在背离难题。为厘清我国财政政策效应的周期特征,本文引入多频谱分析,以极大似然小波分解(MODWT)剔除序列趋势成分的扩张效应干扰,利用带有时变参数的结构向量回归模型(TVP-SVAR)分析我国预算收支和经济波动的关系。结果显示,我国预算收支变化与经济周期趋同,财政政策的实施结果具有顺周期性。具体来看,我国经济增速变化1个单位将导致预算收支分别同方向变化0.7个及0.05个单位以上,预算收入变化1个单位将导致预算支出变化0.9个单位以上。本文还证明预算收入的顺周期属性是导致支出与经济波动顺同的主要影响因素。
检索正文关键字
章节目录
- 一 引言
-
二 文献综述与研究思路
- (一)文献综述
- (二)研究思路
-
三 研究设计和数据说明
- (一)小波分解过程
- (二)模型设定
- (三)数据来源与样本选择
- (四)其他必要说明
-
四 理解我国财政政策与经济周期的波动关系
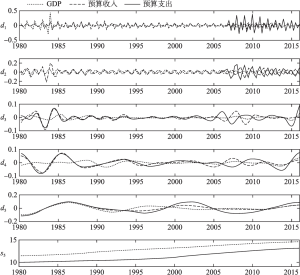
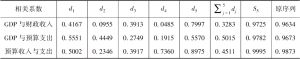
- (一)小波分解结果
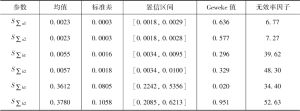
- (二)TVP-SVAR模型的参数检验结果
- (三)基于即期影响系数对我国顺周期政策特征的讨论
- (四)动态脉冲响应分析
- 五 结论与建议
相关文献
查看更多>>>