论文
A Study on the Nonlinear Correlation between the Chinese and US Business Cycles and the Monetary Policy Rule
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 1 Introduction
-
2 Theoretical Analysis and Literature Review
- 2.1 Literature Review
- 2.2 Theoretical Framework
-
3 Re-Estimation of Nonlinear Taylor Rule for China and the US
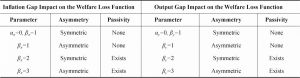
- 3.1 A Taylor Rule Model Accounting for Interest Rate Smoothing
- 3.2 Application of Multiple Threshold Model to the Expanded Taylor Rule
- 3.2.1 Data Processing
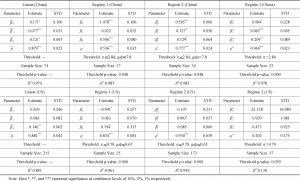
- 3.2.2 Estimating the Multiple Threshold Taylor Rule Model
- 3.2.3 Estimating the Multiple Threshold Taylor Rules Model for China and the US
-
4 A Dynamic Empirical Analysis by LT-TVP-VAR Model
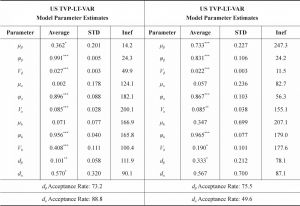
- 4.1 Estimating the Parameter for the LT-TVP-VAR Model
- 4.2 LT-TVP-VAR Based on the New Keynesian Rational Expectations Framework
- 5 Conclusions
相关文献
A Study of Auditing Quality of Branch Offices in the Auditing Market
The Impact of Gambling Behavior on Dividend Payout Policy: Evidence from Taiwan
The Value Relevance of Earnings and Accruals
Global Diversification and Firms’ Stock Market Performance: Do Situational Factors Matter?
Money Market Effect of Open Market Operations: Evidence from China
The Influence of Enterprise Safety Climate on the Safety Behavior of Migrant Workers
查看更多>>>