论文
不幸的道德:运气越差越功利主义
摘要
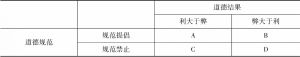
运气是否以及如何影响道德判断?已有研究表明好运气会改善人们的情绪状态,坏运气会增强人们的风险寻求和认知权衡倾向。基于道德双加工理论,情绪与直觉加工驱动的道德规范敏感性相关,认知权衡与理性加工驱动的道德结果敏感性相关。因此,研究假设好运气会增强道德规范敏感性而坏运气会增强道德结果敏感性。本研究启动不同效价的运气之后,使用经预研究检验的组合道德情境材料和CAN算法来测量被试在道德判断中的结果敏感性、规范敏感性和总体接受倾向。结果发现,在结果敏感性上,坏运组显著高于控制组和好运组,但在规范敏感性和总体接受倾向上无显著组间差异。研究表明运气越差越功利主义,在道德判断中越在意结果,初步揭示了运气对道德判断的潜在影响并拓展了道德双加工理论在道德运气研究中的解释。未来研究可以进一步探讨其他形式的运气对道德决策的影响及其心理机制,诱导直觉加工/理性加工状态和操控个体对道德情境的解释水平来深化对道德运气的理论解释。
检索正文关键字
论文目录
- 一 引言
-
二 预研究
- (一)目的
- (二)方法
- 1.被试
- 2.研究材料和研究过程
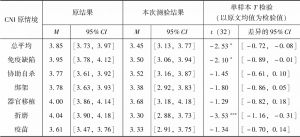
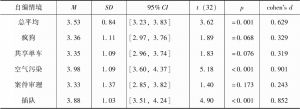
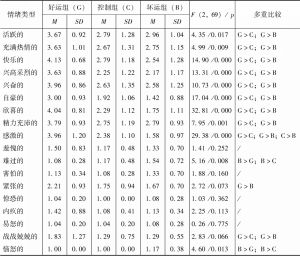
- (三)结果
- (四)讨论
-
三 正式研究
- (一)目的
- (二)方法
- 1.被试
- 2.研究设计
- 3.研究材料与研究过程
- 4.数据处理
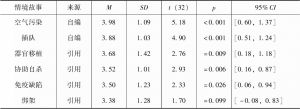
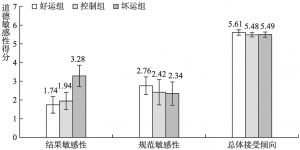
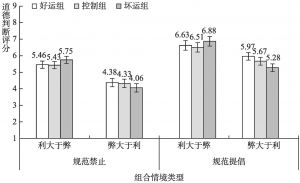
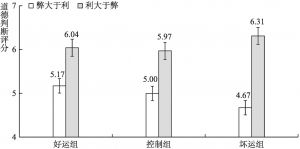
- (三)结果
- (四)讨论
-
四 总讨论
- (一)主要贡献
- (二)局限与未来研究方向
- 五 结论
- 附件一:预研究中故事情境的道德相关性评估材料
- 附件二:中文版规范与结果的组合情境材料
相关文献
宽容对小学生外化问题行为的影响:友谊质量、敌意归因的中介作用
程序公平性和结果有利性对儿童程序正义判断、结果满意度与权威接纳意愿的影响
查看更多>>>